Keyword
CORINE
9 record(s)
Provided by
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Update frequencies
-
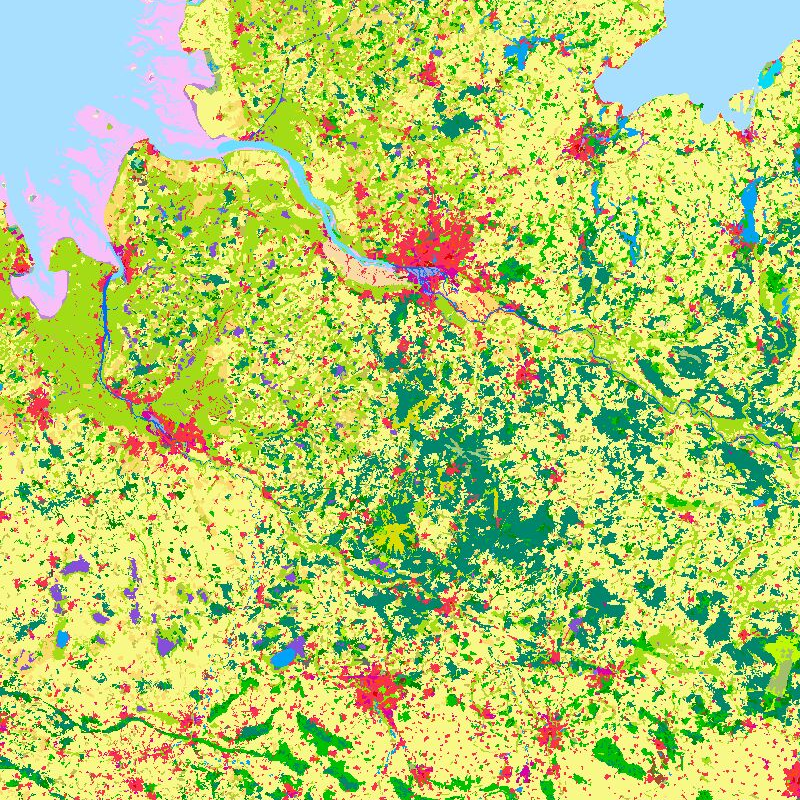
The objective of the pan-European project CORINE Land Cover (CLC) is the provision of a unique and comparable data set of land cover for Europe and the delivery of regular updates to register also the land cover and land use changes over time. It is part of the European Union programme CORINE (Coordination of Information on the Environment). The mapping of the land cover and land use was performed on the basis of satellite remote sensing images. The first CLC data base CLC1990, which was finalized in the 1990s, consistently provided land use information comprising 44 classes, out of which 37 classes are relevant in Germany. The first two updates for Europe were based on the reference years 2000 and 2006. For Germany, DLR-DFD was responsible for the creation of CLC2000 and CLC2006 on behalf of the Federal Environment Agency. In addition to the updated land cover, change datasets were also parts of the project. For deriving a meaningful CLC2000 change product, it became necessary to re-interprete parts of the satellite data of 1990 and to create a revised product, called CLC1990 (rev). Further details: https://www.dlr.de/en/eoc/research-transfer/projects-missions/corine-land-cover
-
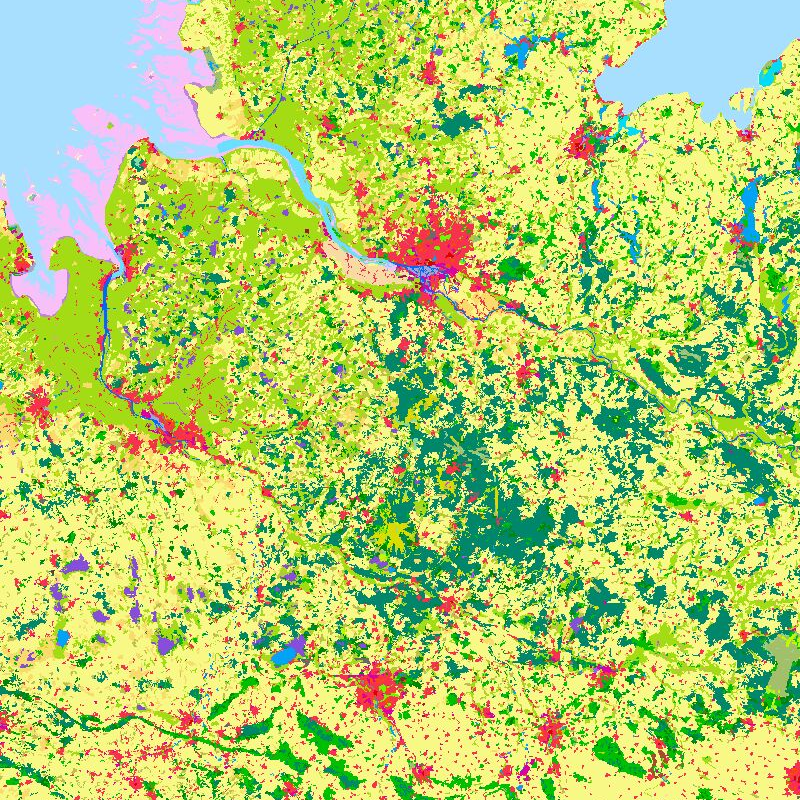
The objective of the pan-European project CORINE Land Cover (CLC) is the provision of a unique and comparable data set of land cover for Europe and the delivery of regular updates to register also the land cover and land use changes over time. It is part of the European Union programme CORINE (Coordination of Information on the Environment). The mapping of the land cover and land use was performed on the basis of satellite remote sensing images. The first CLC data base CLC1990, which was finalized in the 1990s, consistently provided land use information comprising 44 classes, out of which 37 classes are relevant in Germany. The first two updates for Europe were based on the reference years 2000 and 2006. For Germany, DLR-DFD was responsible for the creation of CLC2000 and CLC2006 on behalf of the Federal Environment Agency. In addition to the updated land cover, change datasets were also parts of the project. For deriving a meaningful CLC2000 change product, it became necessary to re-interprete parts of the satellite data of 1990 and to create a revised product, called CLC1990 (rev). Further details: https://www.dlr.de/en/eoc/research-transfer/projects-missions/corine-land-cover
-
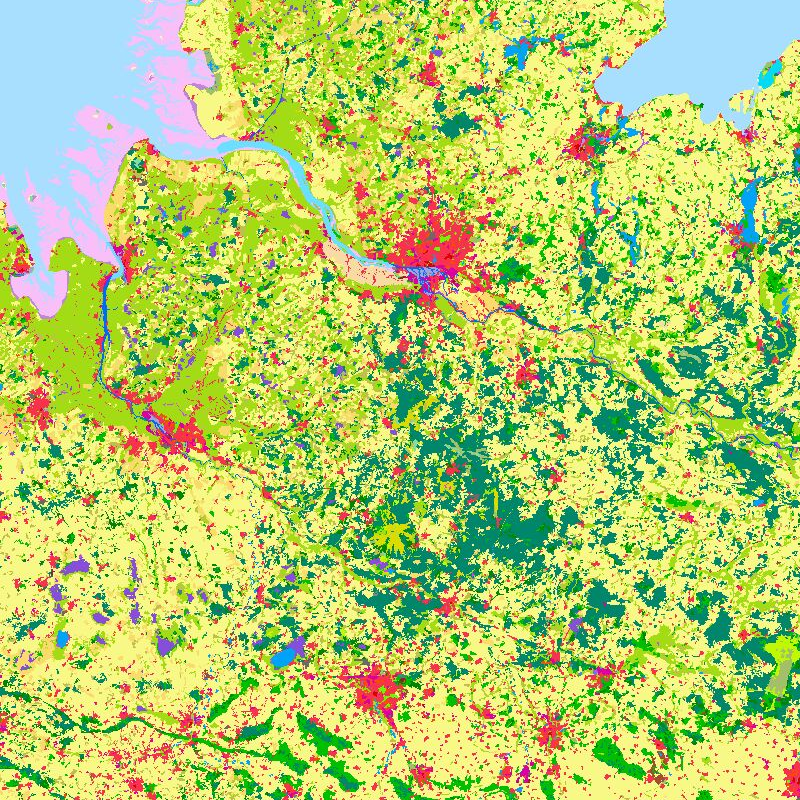
The objective of the pan-European project CORINE Land Cover (CLC) is the provision of a unique and comparable data set of land cover for Europe and the delivery of regular updates to register also the land cover and land use changes over time. It is part of the European Union programme CORINE (Coordination of Information on the Environment). The mapping of the land cover and land use was performed on the basis of satellite remote sensing images. The first CLC data base CLC1990, which was finalized in the 1990s, consistently provided land use information comprising 44 classes, out of which 37 classes are relevant in Germany. The first two updates for Europe were based on the reference years 2000 and 2006. For Germany, DLR-DFD was responsible for the creation of CLC2000 and CLC2006 on behalf of the Federal Environment Agency. In addition to the updated land cover, change datasets were also parts of the project. For deriving a meaningful CLC2000 change product, it became necessary to re-interprete parts of the satellite data of 1990 and to create a revised product, called CLC1990 (rev). Further details: https://www.dlr.de/en/eoc/research-transfer/projects-missions/corine-land-cover
-

The objective of the pan-European project CORINE Land Cover (CLC) is the provision of a unique and comparable data set of land cover for Europe and the delivery of regular updates to register also the land cover and land use changes over time. It is part of the European Union programme CORINE (Coordination of Information on the Environment). The mapping of the land cover and land use was performed on the basis of satellite remote sensing images. The first CLC data base CLC1990, which was finalized in the 1990s, consistently provided land use information comprising 44 classes, out of which 37 classes are relevant in Germany. The first two updates for Europe were based on the reference years 2000 and 2006. For Germany, DLR-DFD was responsible for the creation of CLC2000 and CLC2006 on behalf of the Federal Environment Agency. In addition to the updated land cover, change datasets were also parts of the project. For deriving a meaningful CLC2000 change product, it became necessary to re-interprete parts of the satellite data of 1990 and to create a revised product, called CLC1990 (rev). Further details: https://www.dlr.de/en/eoc/research-transfer/projects-missions/corine-land-cover
-

The objective of the pan-European project CORINE Land Cover (CLC) is the provision of a unique and comparable data set of land cover for Europe and the delivery of regular updates to register also the land cover and land use changes over time. It is part of the European Union programme CORINE (Coordination of Information on the Environment). The mapping of the land cover and land use was performed on the basis of satellite remote sensing images. The first CLC data base CLC1990, which was finalized in the 1990s, consistently provided land use information comprising 44 classes, out of which 37 classes are relevant in Germany. The first two updates for Europe were based on the reference years 2000 and 2006. For Germany, DLR-DFD was responsible for the creation of CLC2000 and CLC2006 on behalf of the Federal Environment Agency. In addition to the updated land cover, change datasets were also parts of the project. For deriving a meaningful CLC2000 change product, it became necessary to re-interprete parts of the satellite data of 1990 and to create a revised product, called CLC1990 (rev). Further details: https://www.dlr.de/en/eoc/research-transfer/projects-missions/corine-land-cover
-
Auf der Grundlage der nutzungsdifferenzierten Bodenübersichtskarte im Maßstab 1:250.000 wird die Feldkapazität bis 1m Tiefe in 5 Klassen abgebildet. Die Feldkapazität ist ein Maß dafür, wieviel Wasser ein Boden dauerhaft gegen die Schwerkraft halten kann. Durch Bezug auf 1m Bodentiefe ergibt sich die Feldkapazität bis 1m unter Geländeoberfläche. Die Maßeinheit ist mm. Die Nutzungsdifferenzierung beruht auf CORINE-Land Cover (CLC5_2018). Die dort aufgeführten Landnutzungsklassen wurden zu 5 Klassen (Acker, Grünland, Wald, Ödland und Siedlung/Verkehr) aggregiert. Die FK1m ist von einer Vielzahl von Faktoren abhängig. Dazu zählen die Bodenart, die Lagerungsdichte, der Humusgehalt und die Nutzung.
-
Auf der Grundlage der nutzungsdifferenzierten Bodenübersichtskarte im Maßstab 1:250.000 wird die nutzbare Feldkapazität bis 1m Tiefe in 5 Klassen abgebildet. Die nutzbare Feldkapazität ist ein Maß dafür, wieviel von Kulturpflanzen nutzbares Wasser ein Boden dauerhaft gegen die Schwerkraft halten kann. Durch Bezug auf 1m Bodentiefe ergibt sich die nutzbare Feldkapazität bis 1m unter Geländeoberfläche. Die Maßeinheit ist mm. Die Nutzungsdifferenzierung beruht auf Corine-Land Cover (CLC5_2018). Die dort aufgeführten Landnutzungsklassen wurden zu 5 Klassen (Acker, Grünland, Wald, Ödland und Siedlung/Verkehr) aggregiert. Die FK1m ist von einer Vielzahl von Faktoren abhängig. dazu zählen die Bodenart, die Lagerungsdichte, der Humusgehalt, und die Nutzung. Die in der Karte dargestellte Mindestflächengröße beträgt 1,5 ha.
-
Auf der Grundlage der nutzungsdifferenzierten Bodenübersichtskarte im Maßstab 1:250.000 wird die Menge an pflanzenverfügbarem Bodenwasser (Wpfl) in 7 Klassen abgebildet. Die Menge an pflanzenverfügbarem Bodenwasser ergibt sich aus Summe von nutzbarer Feldkapazität im effektiven Wurzelraum (nFKWe) und dem Wasser, das den effektiven Wurzelraum durch kapillaren Aufstieg (KA) aus dem Grundwasser erreicht. Die Maßeinheit ist mm. Für die Berechnung des kapillaren Aufstiegs werden Klimadaten der Periode 2001 bis 2020 verwendet. Die Nutzungsdifferenzierung beruht auf CORINE-Land Cover (CLC5_2018). Die dort aufgeführten Landnutzungsklassen wurden zu 5 Klassen (Acker, Grünland, Wald, Ödland und Siedlung/Verkehr) aggregiert. Die Menge an pflanzenverfügbarem Bodenwasser ist von einer Vielzahl von Faktoren abhängig. Dazu zählen die Bodenart, die Lagerungsdichte, der Humusgehalt, und die Nutzung.
-
Auf der Grundlage der nutzungsdifferenzierten Bodenübersichtskarte im Maßstab 1:250.000 wird die nutzbare Feldkapazität im effektiven Wurzelraum in 5 Klassen abgebildet. Die nutzbare Feldkapazität ist ein Maß dafür, wieviel von Kulturpflanzen nutzbares Wasser ein Boden dauerhaft gegen die Schwerkraft halten kann. Die effektive Durchwurzelungstiefe ist ein theoretisch abgeleiteter Wert, der die Tiefe des durchwurzelten Bodenraums beschreibt. Durch Kombination von nFK und We ergibt sich die nutzbare Feldkapazität im effektiven Wurzelraum. Die Maßeinheit ist mm. Die Nutzungsdifferenzierung beruht auf Corine-Land Cover (CLC5_2018). Die dort aufgeführten Landnutzungsklassen wurden zu 5 Klassen (Acker, Grünland, Wald, Ödland und Siedlung/Verkehr) aggregiert. Die nFKWe ist von einer Vielzahl von Faktoren abhängig. Dazu zählen die Bodenart, die Lagerungsdichte, der Humusgehalt, die Gründigkeit, die Nutzung, der Verfestigungsgrad und die Obergrenze von reduzierten Horizonten usw.
 www.geodatenkatalog.de (S1L)
www.geodatenkatalog.de (S1L)