Keyword
Bodenluft
77 record(s)
Provided by
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Update frequencies
Service types
-

-

-
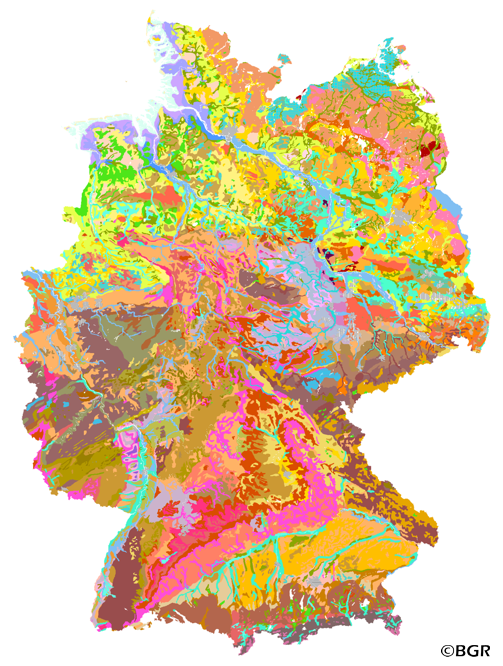
Web Map Service (WMS) of the BUEK1000. The first country wide soil map at a scale of 1:1,000,000 (BUEK1000) has been compiled on the basis of published soil maps of the former German Democratic Republic and the pre 1990 federal states of Germany. To do this, it was necessary to match the soil systems used in East and West Germany and to develop standardized descriptions of soil units. A relatively homogeneous map has resulted, which permits uniform assessment of the soils throughout Germany. The map shows 71 soil mapping units, described in the legend on the basis of the German and FAO soil systems. Each soil unit has been assigned a characteristic soil profile (Leitprofil) as an aid to map interpretation. For the first time the subdivision of the country into 12 soil regions has been represented on the map. This subdivision was coordinated with the state Geological Surveys. These soil regions will represent the highest hierarchic level of nation wide soil maps in future. The colours of soil units correspond to the standards of the 'Bodenkundliche Kartieranleitung' (KA 3; Guidelines for Soil Mapping). The various hues characterize differences in relief or soil humidity. The BUEK1000 was produced digitally. It is an important part of the spatial database integrated in the Soil Information System currently being established at the Federal Institute for Geosciences and Natural Resources (FISBo BGR). It can be used together with the characteristic soil profiles to derive thematic maps related to nation wide soil protection. The scale of the BUEK1000 makes it especially suitable for small scale evaluations at federal or EU level.
-

The first country wide soil map at a scale of 1:1,000,000 (BUEK1000) has been compiled on the basis of published soil maps of the former German Democratic Republic and the pre 1990 federal states of Germany. To do this, it was necessary to match the soil systems used in East and West Germany and to develop standardized descriptions of soil units. A relatively homogeneous map has resulted, which permits uniform assessment of the soils throughout Germany. The map shows 71 soil mapping units, described in the legend on the basis of the German and FAO soil systems. Each soil unit has been assigned a characteristic soil profile (Leitprofil) as an aid to map interpretation. For the first time the subdivision of the country into 12 soil regions has been represented on the map. This subdivision was coordinated with the state Geological Surveys. These soil regions will represent the highest hierarchic level of nation wide soil maps in future. The colours of soil units correspond to the standards of the 'Bodenkundliche Kartieranleitung' (KA 3; Guidelines for Soil Mapping). The various hues characterize differences in relief or soil humidity. The BUEK1000 was produced digitally. It is an important part of the spatial database integrated in the Soil Information System currently being established at the Federal Institute for Geosciences and Natural Resources (FISBo BGR). It can be used together with the characteristic soil profiles to derive thematic maps related to nation wide soil protection. The scale of the BUEK1000 makes it especially suitable for small scale evaluations at federal or EU level.
-
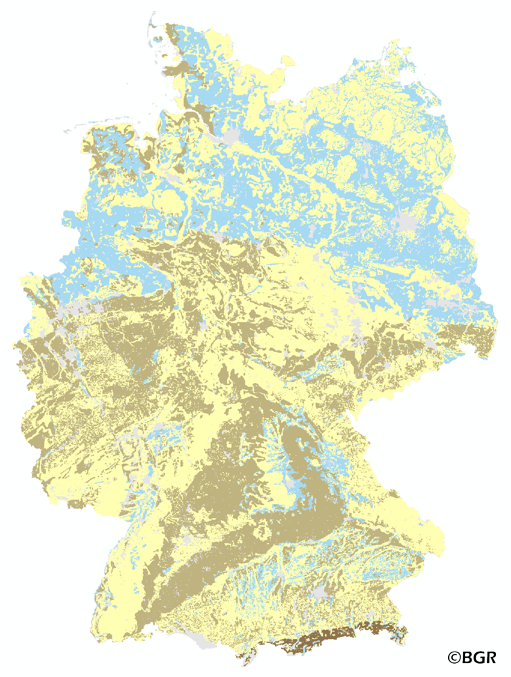
The map of the air capacity of soils in Germany gives an overview of the content of air in a soil at field capacity. The map shows the air, which is available for plant growth from the surface to effective rooting depth, which is derived from land use and soli data. The method is published in the Bodenkundliche Kartieranleitung 4 (1994) and in the documentation of Ad-hoc-AG Boden (representing the soil experts of the geological services of the German federal states). The land use information is derived from the Corine Land Cover data set (2006).
-

The map of the air capacity of soils in Germany gives an overview of the content of air in a soil at field capacity. The map shows the air, which is available for plant growth from the surface to effective rooting depth, which is derived from land use and soli data. The method is published in the Bodenkundliche Kartieranleitung 4 (1994) and in the documentation of Ad-hoc-AG Boden (representing the soil experts of the geological services of the German federal states). The land use information is derived from the Corine Land Cover data set (2006).
-
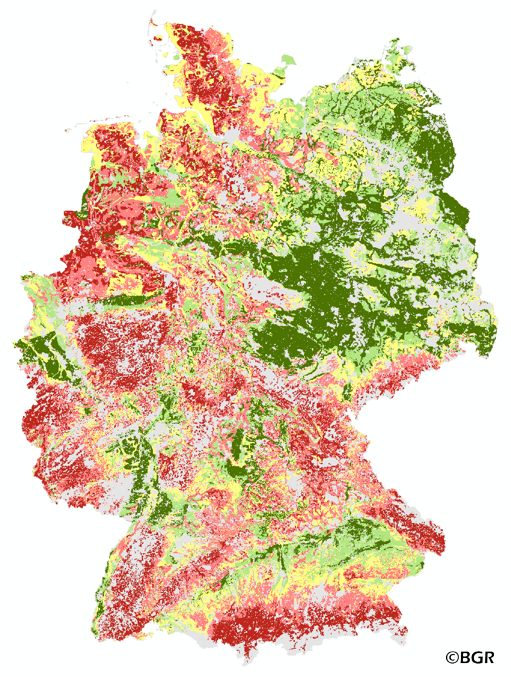
The exchange frequency of water in soils describes how often water and the dissolved substances in it can be replaced in a soil layer during the annual leachate flow. Small water storage capacity means high replacement frequency. The risk of the discharge of easily detachable materials like nitrate is given at high exchange rates.
-

The exchange frequency of water in soils describes how often water and the dissolved substances in it can be replaced in a soil layer during the annual leachate flow. Small water storage capacity means high replacement frequency. The risk of the discharge of easily detachable materials like nitrate is given at high exchange rates.
-
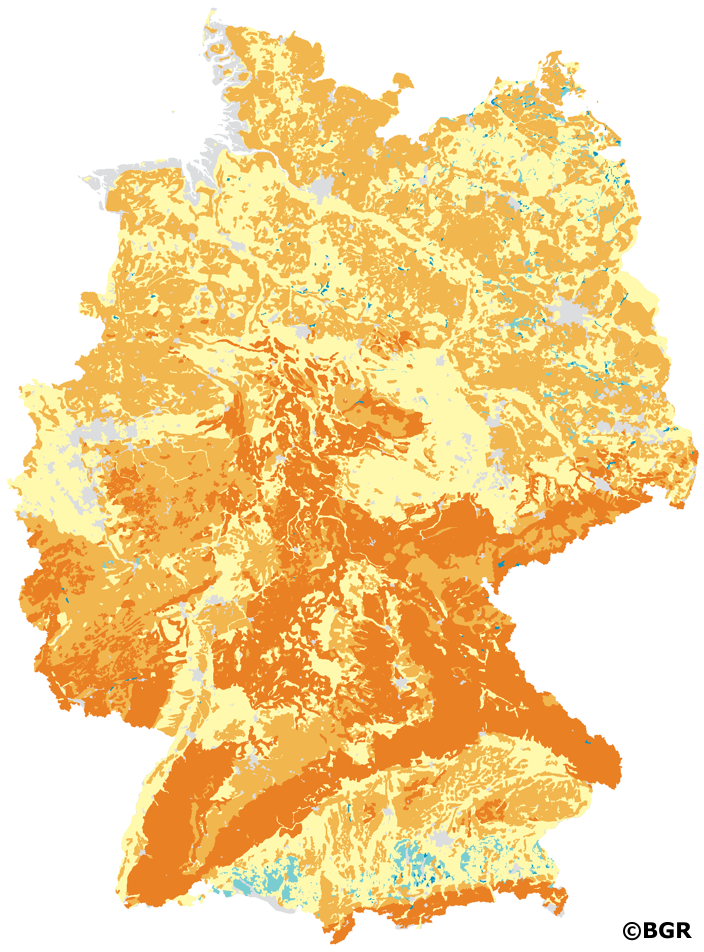
In addition to the natural soil functions, knowledge of the thermal properties of soils is an important parameter for the use of soils, e.g. for near-surface geothermal energy. The heat distribution is largely determined by how quickly the soil conducts energy in the form of heat. How strongly this happens is expressed in the property of thermal conductivity. The thermal conductivity is given in the unit W/(m*K). In addition to the material composition of soil, the water and air balance is decisive. For the present dataset, the soil profiles of the BUEK1000N were evaluated according to the soil science method documentation of the Soil Working Group AG Boden. The soil texture, the dry density and the current water content served as input data. The water content is determined indirectly by deriving the soil moisture from the field capacity and dry density. With G horizons, the total pore volume is also taken into account, with peat only the field capacity. These data are incorporated into soil type-specific equations that take into account the respective properties of sand, clay, silt and loam soils as well as those of peat soils. For solid rock, the rock-specific characteristic values of thermal conductivity are taken from tables. The parameters are determined by horizon. For each legend unit of the BUEK1000N, the dataset gives a minimum and maximum value, the median and a weighted mean value of the thermal conductivity depending on the thickness of the horizons. Settlements, open-cast mining and mudflat areas as well as the areas of landfills, wetlands and bodies of water are not assessed.
-

The water penetrating the soil is of utmost importance for the soil as well as for the environment and for humans. Soils store water and they can also make it available to the plants in a time-delayed manner. How much water the different soils can deliver depends on the soil properties. Part of the precipitation leaves the root zone as percolating water and contributes to groundwater recharge. With the water, nutrients and pollutants are transported in the soil. The theme maps of soil water balance in Germany are based on the landuse stratified soil map of Germany 1:1,000,000 (BUEK1000N), the Digital Elevation Model DGM50 of the German Federal Agency for Cartography and Geodesy (BKG), climatic information of the German Meteorological Service (DWD) for the period 1961-1990 as well as on land use data from the data set CORINE Landcover 2006 (UBA).
 www.geodatenkatalog.de (S2L)
www.geodatenkatalog.de (S2L)