Type
service-view
212378 record(s)
Provided by
Type of resources
Available actions
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Update frequencies
Service types
-
The 1:5 Million International Geological Map of Europe and Adjacent Areas shows the pre-Quaternary geology of Europe onshore and offshore. In addition to the geology attributed by age, petrography and genesis, also magnetic anomalies, tectonic structures, metamorphism and – in the offshore areas – information about the continental/oceanic crust and the continental margin, are shown. The map was developed by BGR under the umbrella of the Commission of the Geological Map of the World (CGMW) and in cooperation with geological surveys organisations of 48 countries and more than 20 research institutes. For detailed information about the 'IGME 5000: More than just a map – A multinational GIS Project' please visit the IGME website.
-
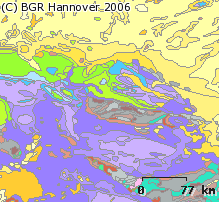
The map shows the average annual groundwater recharge of Germany for the period 1961 - 1990 as a raster image in a cell range of 1 x 1 km. For this purpose, a multi-step regression model was developed (Neumann, J. 2005). In a first step, the baseflow index (BFI = baseflow / total runoff) was determined as the regression target size as a function of slope gradient, drainage density, land cover, available field capacity, depth to groundwater and the ratio of direct runoff to total runoff. Based on this, two different model variants were developed for low-drainage (R 200 mm/a) and high-drainage regions (R 200 mm / a). For R 200 mm/a, groundwater recharge rates were calculated by multiplying the regional grid-based baseflow index and the area-differentiated total runoff according to BAGLUVA. For the higher values R 200 mm/a, a second regression equation has been used which, in addition to the base flow index, also requires the BAGLUVA total runoff and the depth to groundwater.
-
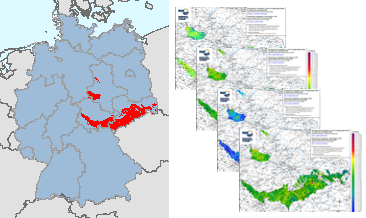
In the former GDR, investigations were carried out between 1980 and 1990 to estimate the raw material potential in the pre-Upper Permian bedrock units (Flechtingen-Rosslau Hills, Harz Mountains, Saxon Granulite Mountains, Thuringian Forest, Thuringian-Vogtlandian Slate Mountains, Ore Mountains, Elbe Valley Region/Lusatia), which lie at the earth's surface or are slightly covered by the Cenozoic. Part of these investigations was a geochemical prospection in the area of the above-mentioned bedrock units. Approximately 18,000 water and 17,500 stream sediment samples were taken and geochemically analysed over an area of almost 15,000 km². The results of these investigations were documented in sub-reports on the individual bedrock units as well as in the "Final Report on the Comparative Evaluation of the Raw Material Potential in the Bedrock Units of the GDR" (Röllig et al., 1990; in German). These data from the bedrock units in the southern part of the former GDR are unique in their high sampling density (more than 1 sample/km²) and provide a comprehensive geochemical survey of these areas. All later geochemical investigations (Geochemical Atlas 2000 as well as within the framework of GEMAS and FOREGS) were carried out with a much lower sampling density. These valuable and irretrievable data are now made generally available via the BGR geoportal. In addition to the digital provision of the original data material, area-wide distribution maps are made available for the first time, which were generated using modern computer-assisted methods. The WMS shows the distribution of the measured element concentrations and parameters in stream waters and stream sediments in four different coloured point and colour shaded contour maps for each element or parameter.
-
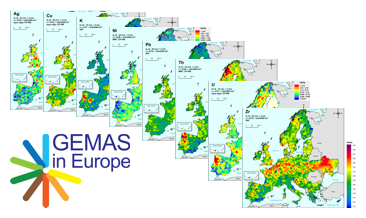
GEMAS (Geochemical Mapping of Agricultural and Grazing Land Soil in Europe) is a cooperative project between the Geochemistry Expert Group of EuroGeoSurveys and Eurometeaux. In total, more than 60 international organisations and institutions worldwide were involved in the implementation of the project. During 2008 and 2009, a total of 2219 samples of agricultural (arable land soils, 0 – 20 cm, Ap samples) and 2127 samples of grazing land (pasture land soils, 0 – 10 cm, Gr samples) soil were collected at a density of 1 site/2 500 km² each from 33 European countries, covering an area of 5,600,000 km². All samples were analysed for 52 chemical elements after an aqua regia extraction, 41 by XRF (total), TC and TOC. In addition, the agricultural soil samples were analysed for 57 elements in a mobile metal ion (MMI®) extraction and Pb isotopes. All analytical results were subject to tight external quality control procedures. The GEMAS project thus provides for the first time fully harmonised data for element concentrations and bioavailability of the elements at the continental (European) scale. The WMS presents the areal distribution of the element contents determined by different analytical methods in the shape of colour shaded contour maps with a classification in 7 and 72 levels each.
-
Between 1977 and 1983, the Federal Institute for Geosciences and Natural Resources (BGR) took approx. 80,000 water samples and 70,000 sediment samples from streams and rivers in several sampling campaigns on the territory of the Federal Republic of Germany at that time and examined them geochemically. In addition to the geochemical prospection of areas with potentially deposits, the aim of the investigations was also to record indications of anthropogenic environmental pollution. The results of these investigations were published in the Geochemical Atlas of the Federal Republic of Germany (Fauth et al., 1985). The data collected within the framework of the Geochemical Atlas of the Federal Republic of Germany in 1985 is a geochemical survey of the former territory of the Federal Republic of Germany which is unique in its high sampling density. All later geochemical investigations were carried out with a much lower sampling density. This valuable and irretrievable data is now being made generally available via the BGR geoportals. In addition to the digital provision of the original data material, the texts from Fauth et al. (1985) and distribution maps produced according to the method used in 1985, the data were reprocessed using modern methods. The WMS shows the distribution of the measured element concentrations and parameters in stream sediments in five different coloured point and colour shaded contour maps for each element or parameter.
-
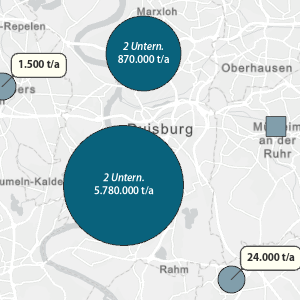
Map service of the Recycling Atlas of the Federal Republic of Germany. The map of the metal recycling sites of the Federal Republic of Germany is published by the German Mineral Resources Agency in the Federal Institute for Geosciences and Natural Resources. It shows the locations of Metal recycling sites for the metals aluminum, lead, precious metals, iron/steel, copper, magnesium, multi-metal (sites that recycle complex metal systems), multi-metal battery (sites that recycle metals from the recovery of complex battery systems), nickel, refractory metals, zinc, tin and mercury. In addition, information such as location capacities and recycling input rates can be queried.
-

The maps "Amplitude anomalies" represent the distribution of gas indicators in the form of amplitude anomalies in seismic data, such as bright spots, gas chimneys, seismically transparent zones and velocity pull-downs. The study area covers the German North Sea sector and the depth range of the first 1,000 m below the seafloor. A wide variety of seismic data was available as a data basis: about 30,000 km of 2D data and about 4,000 km² of 3D data.
-
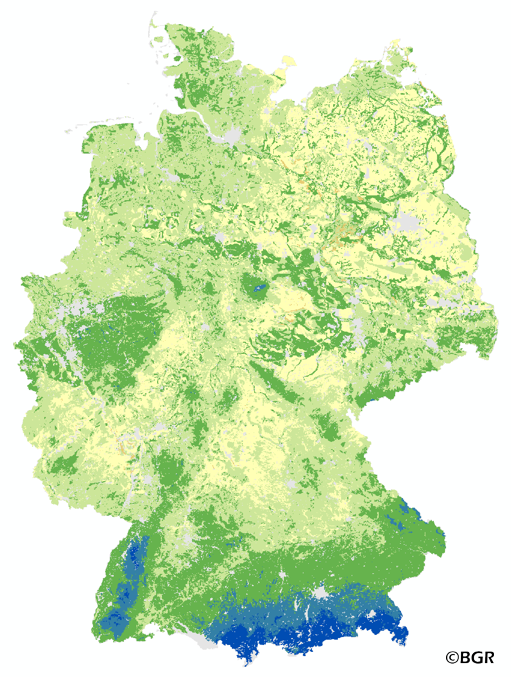
The map of the plant available water in Germany gives an overview of the amount of water which is available for plant growth in the summer period (April – September). It is the sum of the available water holding capacity of soils the precipitation in summer and the amount of capillary rise. The map was made on the basis of the land use stratified soil map of Germany at a scale of 1:1,1000,000, climate data for the period of 1961–1990 and land use information is derived from the Corine Land Cover data set (2006). The method is part of the TUB_BGR approach to model seepage water and is published in the documentation of Ad-hoc-AG Boden (representing the soil experts of the geological services of the German federal states).
-
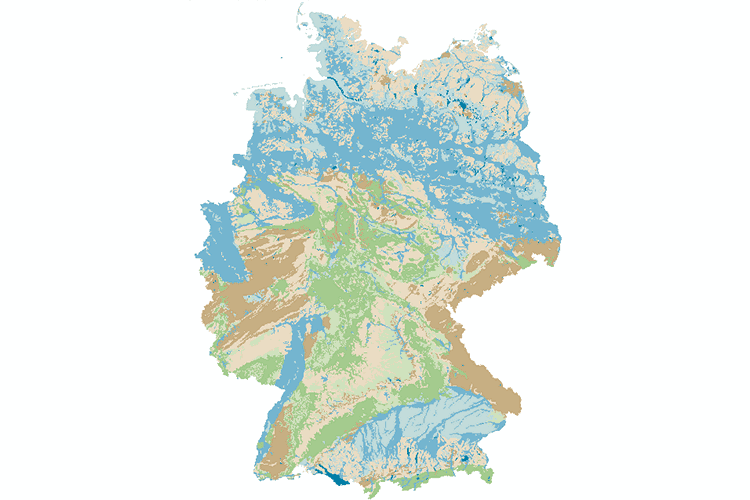
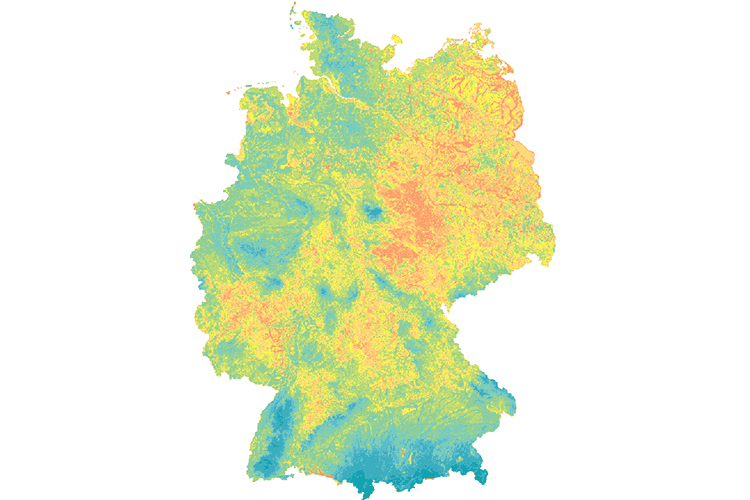
In the original version of the map (Map “Hydrogeology” of the Hydrological Atlas of Germany (HAD)), the surface rocks are first divided into four main types, with further differentiation depending on the extent and productivity. This original subdivision has been resolved applying the internationally widely used Standard Legend for Hydrogeological Maps (SLHyM) after Struckmeier & Margat (1995). This makes the map clearer and easier to read, but above all, it is comparable to other European hydrogeological country and regional maps, such as the International Hydrogeological Map of Europe (IHME1500). The productivity classes have been derived from permeability values. In addition, the surface strata are divided into 19 different types of consolidated or unconsolidated rocks and four types of covering layers. The map is based on the digital Geological Map of Germany 1:1,000,000 (GK1000) published by BGR in 1993.
-
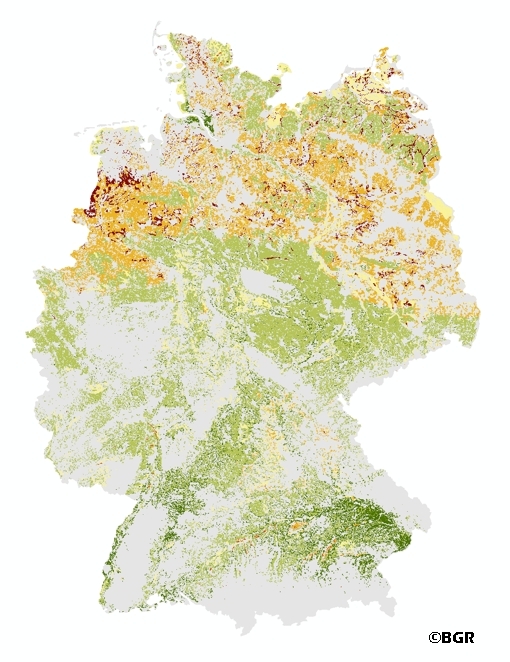
The Potential Wind Erosion Risk map gives an overview of the exposure of arable soils to soil loss due to deflation in Germany. It is based on pedological and climatic factors. The method to predict the soil erosion risk is published in the DIN 19706:2002 and in the documentation of Ad-hoc-AG Boden (representing the soil experts of the geological services of the German federal states). For the application with soil maps, the method was adapted by the Federal Institute for Geosciences and Natural Resources (BGR).The land use stratified soil map of Germany at scale 1:1,000,000 was used as pedological input to the model. The mean annual wind speed at 10 meters above ground level of the period 1980-2000 (DWD) is used as well. The land use information is derived from CORINE land cover data set (2006).
 www.geodatenkatalog.de (S3L)
www.geodatenkatalog.de (S3L)