Catalog

1015 record(s)
Provided by
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Update frequencies
Service types
-

The data set includes meta data of boreholes that are affected by the Geological Data Act and are located within the exclusive economic zone of Germany.
-

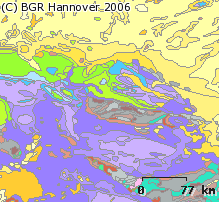
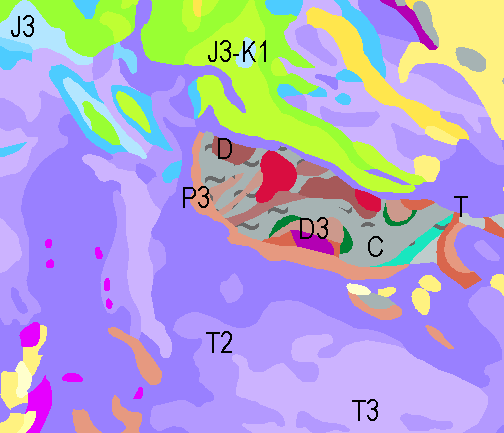
The geological overview map (GÜK200) provides detailed information on the stratigraphy, petrography and genesis of the geological units shown. In the revised GÜK200, the surface geology on the mainland is shown in up to two overlays. The shallow, overlying soil is not shown. In the marine area, only the petrography of the recent seabed is shown, which comprises the uppermost 20 cm of the seabed. In accordance with the original GÜK200 map sheets, the seabed is addressed stratigraphically as recent seabed. The entire map area is dominated by Quaternary formations, whereby a distinction is made between Pleistocene and Holocene deposits. The Pleistocene deposits are dominated by the glacial deposits of the Elster, Saale and Weichselian cold periods, with glacial basin sediments, boulder clay of the ground moraines and glaciofluvial, fluviatile and aeolian deposits. After the end of the glaciations with the rising sea level, the various marine facies, sediments of the land/sea transition zone and on land, above all the fens and raised bogs dominate in the Holocene. Outcrops of older geological units are linked to the dynamics of the Zechstein salts in the subsurface and only occur sporadically in the map area, such as the well-known red sandstone cliffs of Helgoland.
-
The 1:5 Million International Geological Map of Europe and Adjacent Areas shows the pre-Quaternary geology of Europe onshore and offshore. In addition to the geology attributed by age, petrography and genesis, also magnetic anomalies, tectonic structures, metamorphism and – in the offshore areas – information about the continental/oceanic crust and the continental margin, are shown. The map was developed by BGR under the umbrella of the Commission of the Geological Map of the World (CGMW) and in cooperation with geological surveys organisations of 48 countries and more than 20 research institutes. For detailed information about the 'IGME 5000: More than just a map – A multinational GIS Project' please visit the IGME website.
-
The 1:5 Million International Geological Map of Europe and Adjacent Areas shows the pre-Quaternary geology of Europe onshore and offshore. In addition to the geology attributed by age, petrography and genesis, also magnetic anomalies, tectonic structures, metamorphism and – in the offshore areas – information about the continental/oceanic crust and the continental margin, are shown. The map was developed by BGR under the umbrella of the Commission of the Geological Map of the World (CGMW) and in cooperation with geological surveys organisations of 48 countries and more than 20 research institutes. For detailed information about the 'IGME 5000: More than just a map – A multinational GIS Project' please visit the IGME website. Corresponding to the INSPIRE-directive, this dataset comprises the German part of the map.
-

The map of the BGR geoscientific collections displays the localities of the collection‘s objects. Two different types of positions are presented: localities based on available coordinates (´Fundort erfasst´) and subsequently generated coordinates based on descriptions (´Position ermittelt´). The BGR-Geoviewer provides a link directly to the GewiS application (https://gewis.bgr.de) and thus to the description of the collection objects.
-
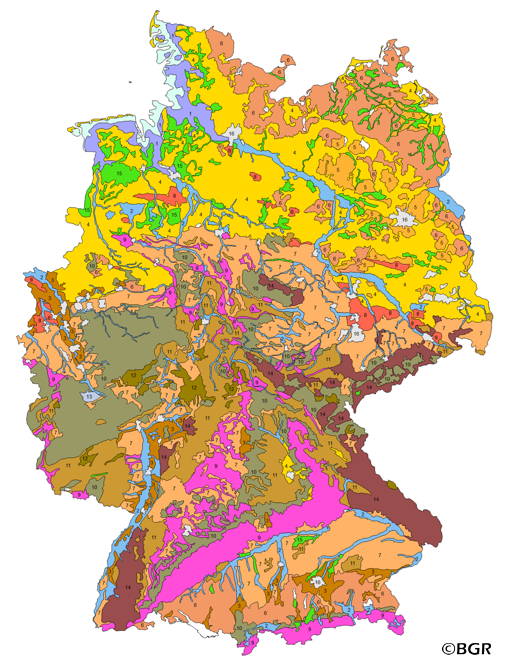
Web Map Service (WMS) of the map Groups of soil parent material in Germany 1:5,000,000. The presented map at scale 1:5,000,000 shows the distribution of 15 soil parent material groups in Germany with polygons of at least 64 square kilometers. Parent material is the rock, from which soil is formed. It was derived from the landuse use stratified soil map of Germany at scale 1:1,000,000. The version 3.0 of the map is based on the Digital Landscape Model 1:1,000,000 (DLM1000) of the Federal Agency for Cartography and Geodesy.
-

For farming, the production function of the soils and thus the natural soil fertility play a decisive role. A healthy soil with its properties, potentials and functions is the basis for high land yields, but at the same time also the basis for sustainable agriculture and responsible land use. The theme maps of soil capability in Germany are based on the landuse stratified soil map of Germany 1:1,000,000 (BUEK1000N), the Digital Elevation Model DGM50 of the German Federal Agency for Cartography and Geodesy (BKG), climatic information of the German Meteorological Service (DWD) for the period 1961-1990 as well as on land use data from the data set CORINE Landcover 2006 (UBA).
-
The map shows the distribution of potential sluiced sand north of the East Frisian Islands. There, primarily sands of medium grain size are needed for the protection of island coasts in order to compensate for the constant coastal erosion caused by rising sea levels, storm surge events and current-induced material removal and transport. The study area is limited to an area bounded on land by the -8 m NN isobath and on sea by the southern traffic separation area ("Terschelling - German Bight"). Large-scale extraction of sluiced sand is only possible down to a depth of 3 m. For future needs, local depth extractions down to a depth of 20 m below the seabed surface may have to be included in the considerations. For the evaluation of the grain size spectrum searched for, 2 maps were prepared. The observation depth differs with regard to the evaluation for a surface sampling to a depth of 3 m and a second one for depth sampling to a depth of 20 m below the seabed. Two classes were kept, showing potential occurrences of sand in the depth ranges mentioned. If the data basis is available in high quality, the general class "sand" was specified and subdivided into "fine to medium sand".
-
The data set includes meta data from sedimentary samples taken within the exclusive economic zone of Germany that are affected by the Geological Data Act. Also includes information on applied laboratory methods.
-

The WMS of the map „Organic Matter Content of Top-Soils in Germany 1:1,000,000 (INSPIRE)“ highlights the results of a Germany-wide compilation of typical soil organic matter contents in top-soils differentiated according to groups of soil parent material, four climatic areas and the main land use. The evaluation is based on more than 9000 soil data profiles with information about Soil Organic Matter (SOM) from a period of about 20 years. The report 'The Organic Matter Content of Top-Soils in Germany', BGR Archive, No. 0127036 (in German) documents the methodology. To transform the organic matter content (of the original dataset HUMUS1000OB) into INSPIRE-relevant organic carbon content (CORG), we applied the van Bemmelen factor (1.724). According to the “Data Specification on Soil“ (D2.8.III.3_v3.0) and the “Guidelines for the use of Observations & Measurements and Sensor Web Enablement-related standards in INSPIRE“ (D2.9_v3.0) the map “Organic Matter Content of Top-Soils in Germany 1:1,000,000“ provides INSPIRE-compliant data. The data has been transformed into the following INSPIRE-Feature Types (Spatial Object Types): “SoilDerivedObject“, “OM_Observation“ and “OM_Process“.
 www.geodatenkatalog.de (S1L)
www.geodatenkatalog.de (S1L)