Keyword
Geophysik
253 record(s)
Provided by
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Update frequencies
Service types
-
Within the framework of DOVE and its topical questions, the project Chatseis combines two seismic methods to increase resolution and reliability of the seismic data; i.e. reflection imaging and full-waveform inversion. To acquire the data for the methodical development and to answer open topical questions, the German Federal Institute for Geosciences and Resources conducted a seismic survey together with the LIAG Institute for Applied Geophysics (LIAG), and the BOKU University Vienna at DOVE site 5068_5 (Bad Aussee). The project team registered seismic P-wave and S-wave data on four profiles (in total approx. 3.5 km, 17.8 GB for P-wave and approx. 2.8 km, 12.7 GB for S-wave).
-
Within the framework of DOVE, the project Chatseis combines two seismic methods to increase resolution and reliability of the seismic data; i.e. reflection imaging and full-waveform inversion. To acquire the optimal data for the tasks in the project Chatseis, the German Federal Institute for Geosciences and Resources conducted two seismic surveys together with the Leibniz Institute for Applied Geophysics and the Bayerisches Landesamt für Umwelt. At the DOVE-site 5068_3 (Schäftlarn), the project team registered seismic P-wave data with explosive and vibration sources and different geophones as well as S-wave data with a small-scale vibratory source and a landstreamer system on three profiles (in total ca 3.8 km, 100 GB for P-wave and ca 2.6 km, 16 GB for S-wave).
-
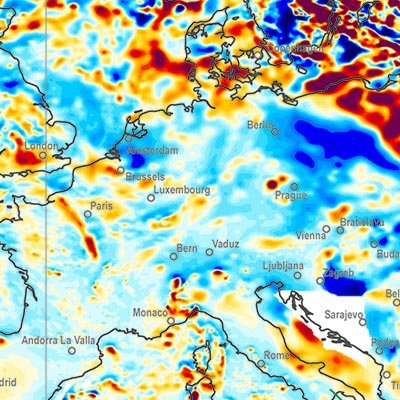
A global Earth Magnetic Anomaly Grid (EMAG2) was compiled from satellite, ship and airborne magnetic measurements. (Maus et al., 2009) Over the continents and the Arctic we made use of exisiting magnetic anomaly grids, whereas original ship and airborne trackline data were processed over the rest of the oceans, wherever available. CHAMP satellite magnetic measurements provided the magnetic field at wavelengths above 330 km. The EMAG2 grid is available at http://geomag.org and http://ngdc.noaa.gov. Directional gridding Due to the sparsity of magnetic field measurements in the southern oceans, it is necessary to interpolate the magnetic field between tracklines. Our interpolation algorithm takes the direction of the magnetic lineations into account. Tje lineations are parallel to the isochrons, which are perpendicular to the gradient of the age of teh oceanic crust. We use the age grid of Müller et al. (2008). The magnetic field ad a given grid point is computet by Least Squares Collocation from the surrounding measurements. If the point is on land, we use an isotropic correlation function with Rc = 14 km correlation length. Over the oceans we use Rc = 56 km parallel to the isochrons and Rc = 14 km in the spreading direction. Measurements seperated from the grid point by an age discontinuity or a topographic feature are excluded from the collation.
-
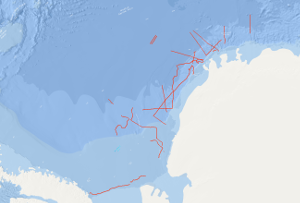
On the F.S. POLARSTERN cruise ANT-IV/3 (6th December, 1985 - 13th March, 1986) multichannel seismic measurements were carried out in parallel with magnetic and gravimetric measurements on 33 lines with a total length of 6,263 km. 3,350 km of the multichannel seismic lines have been processed aboard. The geophysical studies were designed to investigate the structure and geological development of the Weddell Sea continental margin from meridians zero to 60°W, and to define suitable and safe drilling locations for Leg 113 of the Ocean Drilling Program. The main results of the geophysical studies are: (1) The discovery of an approximately N50°E trending failed drift basin, following the trend of a negative magnetic anomaly and a positive gravity anomaly. (2) The discovery of two extensive wedge-shaped and symmetric basement units around a failed drift basin between longitudes 40°W and 20°W. The seismic characteristics, i.e. seismic velocities of 4 km/s and an internally divergent pattern of reflectors suggest that both wedges are formed from extrusive/intrusive volcanic rocks. (3) The confirmation of a major plate tectonic boundary trending approximately N80°E to N60°E, i.e. the EXPLORA-ANDENES escarpment. (4) The confirmation of a glaciogenic progradational wedge beneath the shelf of the Weddell Sea Embayment, made up of several thousand metres of sediments. (5) The definition of 13 suitable and safe drilling locations for ODP-Leg 113.
-
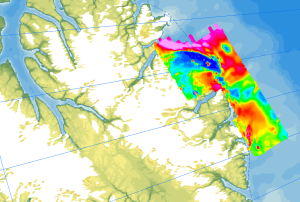
Onshore geological field work combined with an onshore/offshore aeromagnetic survey was carried out during a joint expedition of the German BGR and the Canadian GSC to understand the structural architecture of the North American continental margin. The helicopter-borne magnetic survey of 2008 covered the northern coastal areas of Ellesmere Island and the adjacent marine areas. The survey was conducted with a line separation of 2 km and covered a 40 to 50 km wide swath offshore about parallel to the north coast of Ellesmere Island from Yelverton Bay in the west to Parr Bay east of Cape Columbia, the northernmost point of Canada. Between Yelverton Bay and M'Clintock Inlet, the survey extended about 40 to 50 km inland, which was the prime target area of the CASE 11 geological investigations. This section of mountainous terrain was flown in a “draped” mode to keep the distance to ground at approximately 1500 ft, same as over the offshore areas. During a 4-weeks period in May/June 2008, close to 8000 km of aeromagnetic line data were acquired, covering an area of 12000 km².
-
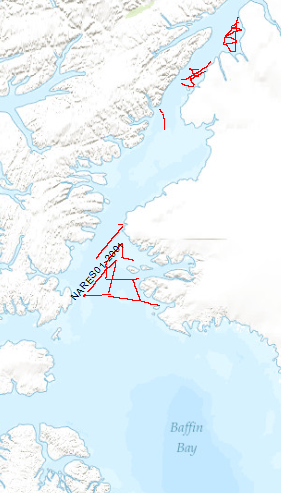
The Scientific staff and crew onboard CCGS Louis S. St. Laurent (LSL) returned September the 10th, 2001 from a scientific expedition to the Nares Strait, the northernmost waterway connecting the Arctic and Atlantic oceans. The data format is Society of Exploration Geophysicists SEG Y. The ice conditions in the strait required the support of Canada's largest ice breaker. The ship was a versatile platform for 34 scientists to accomplish their marine investigation. The LSL has a history of supporting international scientific expeditions including an oceanographic transect of the Arctic Ocean in 1994 and a biological study of the Canadian Arctic Islands in 1999. Germany (Bundesanstalt für Geowissenschaften und Rohstoffe, BGR) and Canada (Geological Survey of Canada) undertook a 5-week scientific cruise to study and explore the geological structure and evolution of the Nares Strait. The primary objective was the study of structural features relating to the formation of the Arctic Ocean and, in particular, the study of the Wegener Fault. This fault is a linear boundary between Greenland and Ellesmere Island which was noted by the German scientist Alfred Wegener in 1915 and later became the subject of a major scientific controversy. The co-operative cruise, which was planned over a period of 2 years, provided the basis for a wide range of scientific investigations, from marine seismic work and climate change studies through airborne magnetic investigations to geodetic survey measurements and geological sampling onshore. Systematic geophysical offshore studies in this key area had not been undertaken before. Where towing of seismic equipment was not possible because of ice coverage, magnetic maps were made using a helicopter-borne magnetic sensor system. Sediment and water samples taken during the cruise provide information on changes in climate and sea ice cover from the last ice-age to the present. An 11 m-long sediment core from outer Jones Sound is the longest core ever taken in the Canadian Arctic channels and holds clues to the detailed climate history of northern Baffin Bay.
-
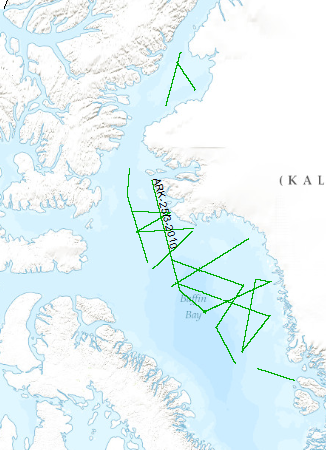
The multidisciplinary marine geoscientific expedition ARK-25/3 was focused on the Greenland part of northern Baffin Bay and was aimed to acquire new geoscientific data to be used for modelling the evolution of the Greenland continental margin and its hydrocarbon prospective. The data format is Society of Exploration Geophysicists SEG Y. The cruise was performed under the direction of the Federal Institute for Geosciences and Natural Resources Hannover in cooperation with the Alfred-Wegener-Institute for Polar and Marine Research, Bremerhaven. Using 70 days of ship time onboard the research icebreaker R/V POLARSTERN a comprehensive data set was acquired along profiles extending from the deep oceanic basin in the central part of North Baffin Bay onto the Greenland continental margin in an area which was bordered by the Kane Basin in the North and Disko Island in the South. By means of multi-channel seismic, wide angle seismic, gravimetric and magnetic methods the structural inventory of the crust in the NW Baffin Bay was investigated. Additionally, heat flow data and sediment cores were collected along lines crossing the Greenland continental margin. The cores were extracted for geochemical and geomicrobiological analysis to be used for basin modelling, studying the hydrocarbon potential, and the hydrocarbon degradation by microorganisms under polar conditions. Geological sampling in the coastal area was done between Melville Bay and Washington Land. The collected rock material will be used to derive constraints on the erosion history of the coastal area. Aeromagnetic data was acquired covering a substantial part of the marine survey area to investigate magnetic signatures of the oceanic crust and the continental margin. This report summarizes the working programme and contains the documentation of acquired data and first results of the expedition.
-
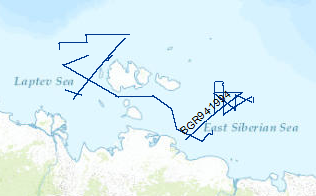
On the M/V Akademic Nemchinow multichannel seismic measurements were carried out on 34 lines with a total length of 4,000 km. The area covered was the Laptev Sea. The data format is Society of Exploration Geophysicists SEG Y.
-
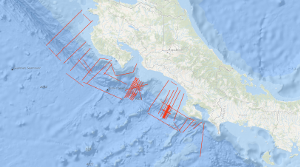
Between 08.11.1999 and 02.12.1999 the active convergent margin off Costa Rica was investigated using the S/V Professor Polshkov. The cruise had three scientific targets. Several seismic profiles in the dip-direction of the subduction zone were acquired to map the general variability of the accretionary wedge. Near the Jaco Scarp, a dense net of seismic profiles using a smaller seismic source should deliver information about the amount of gas hydrates within the shallow sub-surface. In an area of this wedge south of the Quepos Plateau densely spaced seismic lines were measured to prepare an ODP campaign (which was finished in 2011 as IODP Expedition 334).
-
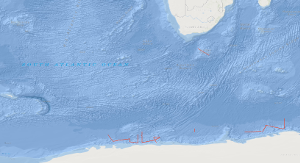
The BGR Antarctic cruise 1996 from 29th December 1995 to 6th February 1996 with M.S. AKADEMIK NEMCHINOV was designed to acquire new marine geophysical data for a better understanding of the geological processes, timing, occurrence and location of rifts of the initial break-up of southern Gondwanaland. A total of 3,836 km of multichannel seismic reflection data have been collected in the areas of the Cosmonaut Sea, the Astrid Ridge, the Lazarev Sea and the southern Agulhas Plateau in parallel with magnetic and gravity measurements. In addition magnetic and gravity measurements were carried out on transit. Major new observations of the collected MCS data include: (1) Volcanic rocks play a major part in the construction of the Astrid Ridge and also of the Agulhas Plateau. (2) The early opening of the Lazarev Sea was associated with excessive volcanism resulting in the emplacement of a voluminous volcanic body characterized by an internally divergent pattern of seaward-dipping reflectors. (3) The Astrid Fracture Zone continues in form of a sediment-filled basement depression flanked by distinct basement highs into the Lazarev Sea, and apparently swings to the west parallel to the coast of Queen Maud Land. (4) The thickness of sediments in the Cosmonaut Sea overlying oceanic crust of inferred Early Cretaceous age is in excess of 4s (twt), i.e. about 6,000 m. Three regional seismic markers of inferred Cretaceous, Late Eocene-Oligocene and Middle Miocene ages subdivide the sedimentary column.
 www.geodatenkatalog.de (S3L)
www.geodatenkatalog.de (S3L)