Keyword
geophysics
91 record(s)
Provided by
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Update frequencies
Service types
-
-
Two strong eruptions of Stromboli Volcano (38.789°N 15.213°E, 920 m) occurred on July 3rd and August 28th 2019. This data set provides the infrasound records in terms of raw pressure data in Pascal of both eruptions available at BGR’s infrasound array I26DE in Germany as well as infrasound arrays OHP and CEA in France. The publication “Using dense seismo-acoustic network to provide timely warning of the 2019 paroxysmal Stromboli eruptions” (Le Pichon et al., 2021, Scientific Reports) provides further details on this data set and its scientific application. Data format: The data are provided as ASCII files (separate file for each infrasound sensor and hour of measurement, plus a README file).
-
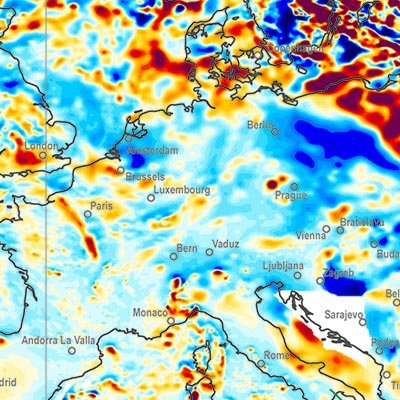
A global Earth Magnetic Anomaly Grid (EMAG2) was compiled from satellite, ship and airborne magnetic measurements. (Maus et al., 2009) Over the continents and the Arctic we made use of exisiting magnetic anomaly grids, whereas original ship and airborne trackline data were processed over the rest of the oceans, wherever available. CHAMP satellite magnetic measurements provided the magnetic field at wavelengths above 330 km. The EMAG2 grid is available at http://geomag.org and http://ngdc.noaa.gov. Directional gridding Due to the sparsity of magnetic field measurements in the southern oceans, it is necessary to interpolate the magnetic field between tracklines. Our interpolation algorithm takes the direction of the magnetic lineations into account. Tje lineations are parallel to the isochrons, which are perpendicular to the gradient of the age of teh oceanic crust. We use the age grid of Müller et al. (2008). The magnetic field ad a given grid point is computet by Least Squares Collocation from the surrounding measurements. If the point is on land, we use an isotropic correlation function with Rc = 14 km correlation length. Over the oceans we use Rc = 56 km parallel to the isochrons and Rc = 14 km in the spreading direction. Measurements seperated from the grid point by an age discontinuity or a topographic feature are excluded from the collation.
-
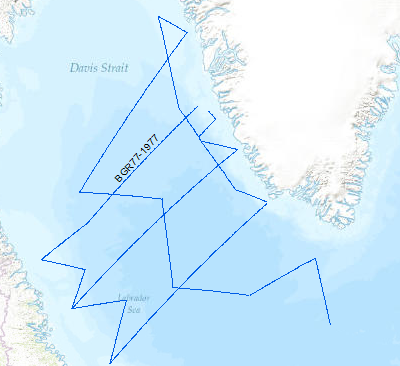
A geophysical reconnaissance survey was carried out in the Labrador Sea and Davis Strait between July and September 1977 by BGR. The data format is Society of Exploration Geophysicists SEG Y. The survey was executed on the research vessel MS Explora. The seismic, magnetic and gravity data from 5931 line-kilometers on 21 lines were recorded on magnetic tape. A 24-fold coverage technique was used with 48 seismic channels (traces), with a 2400m streamer cable, and 23.45 l airgun array. A full integrated computerized satellite navigation system (INDAS III) served as positioning system. Based on a preliminary interpretation of the seismograms, the Labrador Sea was devided into an eastern (Greenland) and western (Canadian) area, seperated by the Mid Labrador Ridge. Within the eastern part of the Labrador Sea the Pre-Cenozoic sediments show three distinct layers, traceable over the entire Greenland area of the sea. In the Cenozoic layer olisthostromes occur. The highest apparent velocity determined from sonobuoy data was 9.26 km/sec. The calculated refractor lies at a depth of approximately 13 km. The seismic section from the sediments on the Canadian side of the Labrador Sea show a uniform series of thick sediments below the Cenozoic cover. The highly disturbed basement is often masked by the multiple reflections from the seafloor. Statements about the nature and structure of the basement can only be made after processing data.
-
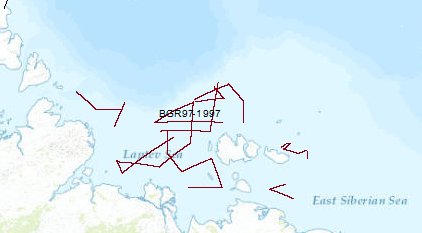
The 3rd cooperative BGR/SMNG Arctic cruise was designed to acquire new scietific data for a better understanding of temporal and spatial lithospheric variations during rifting and its influence on the tectonic and structural evolution of the continental crust of the Laptev Sea undergoing extension since at least the Early Tertiary, and for tackling open questions regarding the evolution of the submarine permafrost zone. Although conditions for seismic measurements were worse in 1997 than in 1993 and 1994, along 4,622 km of seismic traverses reflection seismic data and wide angle reflection/refraction data from 23 OBH-(ocean bottom hydrophone) stations were collected in the Laptev and East Siberian Sea. The most prominent rift basin is the Ust' Lena Rift, which is at least 300 km wide at latitude 75°N. The Cenozoic sedimentary cover exceeds 3 km everywhere, increasing up to 14 km at two locations. In the northern part of the shelf, the complex mainly N–S-trending Anisin Basin has a basin fill of up to 10 km thickness. The New Siberian Basin which is located in the northwestern part of the study area shows an up to 9 km thick graben fill. The Laptev Horst crust is locally subdivided into several tilted blocks by deep-reaching faults and there are several half grabens of smaller extent which divide the Laptev Horst into three parts: the North, the South and the East Laptev Horst. A major west dipping listric fault of at least 250 km length separates the Laptev Horst from the Ust' Lena Rift. Results from the seismological investigation indicate that recent extension is concentrated within the narrow rift basins of the eastern Laptev Sea. From wide-angle reflection/refraction seismic measurements the seismic velocities of the crustal layers were estimated along five profiles. The layers with velocities of up to 3.5 km/s apparently consist of predominantly Cenozoic sediments. The sedimentary section showing relatively high seismic velocities of 4.5 to 5.2 km/s might be interpreted as Late Paleozoic to Mesozoic deposits or overcompacted/cemented syn-rift deposits. In the eastern shelf area a layer beneath the acoustic basement was interpreted to represent Ordovician to Early Mesozoic carbonates. The lower crust in the area under study shows relatively uniform seismic velocities of about 6.0-6.8 km/s and the velocities estimated for the crust-mantle transition are in the range of 8.0 to 8.2 km/s. The origin of a several 100 m thick layer with a relative high velocity of 3 to 3.5 km/s directly beneath the seafloor was inferred as sub-sea permafrost.
-
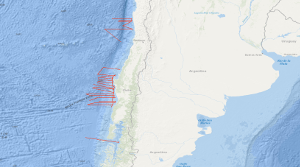
Within the frame of the comprehensive SPOC project (Subduction Processes off Chile) the SONNE cruises SO161 Leg 2 and 3 have been conducted between October 16th and November 29th, 2001, off central Chile between 28° and 44° S. In that period some 5,300 km were surveyed with multichannel seismic (MCS) reflection, magnetic, gravity, high-resolution bathymetric and echographic methods. In addition, approximately 3,900 km were surveyed with the same spectrum of methods but without MCS. The total number of 2D profiles was 48. Target was the variation of the subduction properties between the convergent oceanic Nazca and continental Southamerica plates and the different conditions that might influence the subduction process as there are: (1) age of the oceanic crust, (2) its structure and composition, (3) its sedimentary cover, (4) its thermal state, (5) the subduction angle and obliquity, and (6) the terrigenous sediment afflux from the continent. Furthermore, special focus was given to the subduction front, the subduction interface, the structure of the slope as well as to the forearc basin structure and history, and the general distribution of gas hydrate indicating bottom simulating reflectors (BSR's). The results are to be compared with previous studies of the Chilean active margin, e.g. CONDOR (SO 101 and 103) and CINCA (SO 104). The SPOC target area was subdivided into three sub-areas A,B and C. One area was chosen for a detailed survey by aid of a narrowly spaced grid and for a close link with a lot of partners. This area is characterized by a distinctly different margin type south of it is assumed. Moreover, the subducting portion of the aseismic Juan Fernandez Ridge is located in that area representing another important target of the survey. Advantageous conditions enabled the survey of an east-west profile south of Chiloé Island, providing a section through the submerged coastal Cordillera into the flooded longitudinal valley. Some results of Leg 2 and 3 are: In all areas A, B and C no subduction bulge (outer high) in the oceanic crust was visible perhaps due to the shortness of the profiles. The sedimentary cover of the oceanic crust is exceptionally thin, and the crustal thickness is generally quite "normal" with around 7 km derived from relatively weak Moho reflections. In area B a so far magnetically unmapped region was filled providing reliable ages of the oceanic crust, and suggesting that the Challenger Fracture Zone abruptly terminates west of the area of investigation. The survey in area C yielded valuable information on the trench morphology. The so far unique MCS profile south of Chiloé island shows a very wide trench and allows to extrapolate the general conditions encountered an area A southward to approximately 44° S. It can be stated that the situation is in sharp contrast to the basin structures detected by industry profiles further north in the Golfo de Corcovado.
-
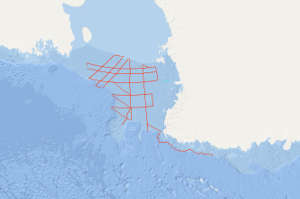
During the cruise with S.V. EXPLORA within the Ross Sea on the second marine-geophysical expedition of the Federal Institute for Geosciences and Natural Resources (BGR) to Antarctica, in total 6,745 km of magnetic, gravity and digital reflection seismic lines and additionally 1,400 km gravity lines were acquired in the period from January 10th to March 2nd 1980. On 43 stations sonobuoy refraction measurements have been carried out. The main results are: (1) In the eastern part of the Ross Sea Shelf two striking discontinuities have been identified in the reflection seismics representing gaps in the sediments at the turn-over of the Upper Miocene to the Pliocene (ca. 7 mio years B.P.) and between the Middle and Upper Miocene (ca. 11.5 mio. years B.P.) according to results of DSDP boreholes. (2) In the southern part of the Ross Sea Shelf the basement is uncovered at depths over 700m due to a thrust of the shelf ice recently. (3) A structural unit extends alongside the meridian of 180° separating the Ross Sea into two different geologic regions. This unit is characterised by two basement highs with seismic velocities exceeding 5 km/sec. (4) In relation with the GANOVEX expedition two profiles have been measured off northern Victoria Land which indicate two large faults with a faulting amount of 2 km. Another area is characterised by intrusive and volcanic bodies.
-
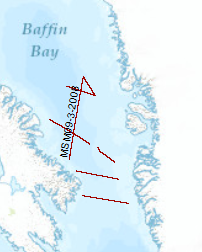
The cruise leg MSM09/3 was conducted as a cooperative project between the Alfred Wegener Institute for Polar and Marine Research (AWI), the Federal Institute for Geosciences and Resources (BGR), the Geological Survey of Denmark and Greenland (GEUS) and Dalhousie University. The data format is Society of Exploration Geophysicists SEG Y. A geophysical survey covered areas of Baffin Bay and Davis Strait between Greenland and the Canadian Baffin Island. A component of the IPY 2007/08 Lead Project Plate Tectonics and Polar Gateways in the Earth System (PLATES & GATES), this project DAVIS GATE is aimed to develop a tectonic and sedimentary reconstruction of the opening process of this oceanic gateway. Baffin Bay and Davis Strait play an important role in the shallow water exchange from the Arctic to the Atlantic Ocean. The plate-tectonic evolution as well as the magmatic history of this region has been sparsely known and required a careful geophysical investigation in order to construct a set of gridded detailed paleotopographic maps for a complete geodynamic reconstruction of this gateway. With a set of three seismic refraction/wide-angle reflection profiles, using ocean-bottom seismometers on 62 stations, as well as multi-channel reflection seismic recordings with a 3000-m long streamer, data were acquired from the sedimentary cover to the deep crust and even from parts of the uppermost mantle. Additional seismic data supplement these profiles and provide insights into the structures of the basement and dominant fault zones such as the Ungava fault system. A parallel running magnetic survey aimed to resolve the temporal evolution of the oceanic crust of Baffin Bay. The extension and subsidence of the continental and transitional crust in the Davis Strait and the evolution of oceanic crust in the Labrador Sea and Baffin Bay could be investigated with dataset to which continuously recorded gravity anomaly data and sub-bottom profiler data also contribute. This dataset provides the basis of geometrical and physical properties of the crust required for a realistic geodynamic model which will describe the break-up and the ocean basin evolution between Greenland and Canada in terms of detailed paleo-topography.
-
Rocket launches for space missions are well-defined ground-truth events generating strong infrasonic signatures. This data set covers ground-truth information for 1001 rocket launches from 27 global spaceports between 2009 and mid-2020. Infrasound signatures from up to 73% of the launches were identified at infrasound arrays of the International Monitoring System. The detection parameters were obtained using the Progressive Multi-Channel Correlation (PMCC) algorithm. Propagation and quality parameters supplement the PMCC detection parameters in this dataset. The results are provided for further use as a ground-truth reference in geophysical and atmospheric research. The open-access publication “1001 Rocket Launches for Space Missions and their Infrasonic Signature” (Pilger et al., 2021, Geophys. Res. Letters, doi:10.1029/2020GL092262) provides further details on this data set. Data format: The data are provided both as ASCII files (separate lists of infrasound signatures and rocket launch events, plus README files) and as a comprehensive netCDF file.
-
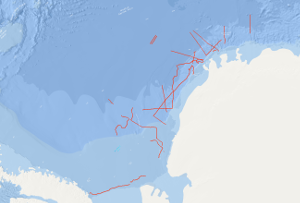
On the F.S. POLARSTERN cruise ANT-IV/3 (6th December, 1985 - 13th March, 1986) multichannel seismic measurements were carried out in parallel with magnetic and gravimetric measurements on 33 lines with a total length of 6,263 km. 3,350 km of the multichannel seismic lines have been processed aboard. The geophysical studies were designed to investigate the structure and geological development of the Weddell Sea continental margin from meridians zero to 60°W, and to define suitable and safe drilling locations for Leg 113 of the Ocean Drilling Program. The main results of the geophysical studies are: (1) The discovery of an approximately N50°E trending failed drift basin, following the trend of a negative magnetic anomaly and a positive gravity anomaly. (2) The discovery of two extensive wedge-shaped and symmetric basement units around a failed drift basin between longitudes 40°W and 20°W. The seismic characteristics, i.e. seismic velocities of 4 km/s and an internally divergent pattern of reflectors suggest that both wedges are formed from extrusive/intrusive volcanic rocks. (3) The confirmation of a major plate tectonic boundary trending approximately N80°E to N60°E, i.e. the EXPLORA-ANDENES escarpment. (4) The confirmation of a glaciogenic progradational wedge beneath the shelf of the Weddell Sea Embayment, made up of several thousand metres of sediments. (5) The definition of 13 suitable and safe drilling locations for ODP-Leg 113.
 www.geodatenkatalog.de (S1L)
www.geodatenkatalog.de (S1L)