Keyword
Zechstein
19 record(s)
Provided by
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Update frequencies
Service types
-

Which salt formations are suitable for storing hydrogen or compressed air? In the InSpEE-DS research project, scientists developed requirements and criteria for the assessment of suitable sites even if their exploration is still at an early stage and there is little knowledge of the salinaries’ structures. Scientists at DEEP.KBB GmbH in Hanover, worked together with their project partners at BGR and the Leibniz University Hanover, Institute for Geotechnics, to develop the planning basis for the site selection and for the construction of storage caverns in flat layered salt and multiple or double saliniferous formations. Such caverns could store renewable energy in the form of hydrogen or compressed air. While the previous project InSpEE was limited to salt formations of great thickness in Northern Germany, salt horizons of different ages have now been examined all over Germany. To estimate the potential, depth contour maps of the top and the base as well as thickness maps of the respective stratigraphic units were developed. Due to the present INSPIRE geological data model, it was necessary, in contrast to the original dataset, to classify the boundary lines of the potential storage areas in the Zechstein base and thickness layers, whereby the classification of these lines was taken from the top Zechstein layer. Consequently, the boundary element Depth criterion 2000 m (Teufe-Kriterium 2000 m) corresponds on each level to the 2000 m depth of Top Zechstein. However, the boundary of national borders and the boundary of the data basis could not be implemented in the data model and are therefore not included in the dataset. Information on compressed air and hydrogen storage potential is given for the identified areas and for the individual federal states. According to the Data Specification on Geology (D2.8.II.4_v3.0) the content of InSpEE-DS (INSPIRE) is stored in 18 INSPIRE-compliant GML files: InSpEE_DS_GeologicUnit_Isopachs_Zechstein.gml contains the Zechstein isopachs. InSpEE_DS_GeologicUnit_Isobaths_Top_Zechstein.gml and InSpEE_DS_GeologicUnit_Isobaths_Basis_Zechstein.gml contain the isobaths of the top and basis of Zechstein. The three files InSpEE_DS_GeologicStructure_ThicknessMap_Zechstein, InSpEE_DS_GeologicStructure_Top_Zechstein and InSpEE_DS_GeologicStructure_Basis_Zechstein represent the faults of the Zechstein body as well as at the top and at the basis of the Zechstein body. InSpEE_DS_GeologicUnit_Boundary_element_Potential_areas_Zechstein.gml contains the boundary elments of the potential areas at the top and the basis of Zechstein as well as of the Zechstein body. The three files InSpEE_DS_GeologicUnit_Uncertainty_areas_ThicknessMap_Zechstein.gml, InSpEE_DS_GeologicUnit_Uncertainty_areas_Top_Zechstein.gml, InSpEE_DS_GeologicUnit_Uncertainty_areas_Basis_Zechstein.gml represent the uncertainty areas of the Zechstein body as well as at the top and at the basis of the Zechstein body. InSpEE_DS_GeologicUnit_Potentially_usable_storage_areas_Storage_potential_in_the_federal_states.gml comprises the areas with storage potential for renewable energy in the form of hydrogen and compressed air. The six files InSpEE_DS_GeologicUnit_Salt_distribution_in_Germany_Malm.gml, InSpEE_DS_GeologicUnit_Salt_distribution_in_Germany_Keuper.gml, InSpEE_DS_GeologicUnit_Salt_distribution_in_Germany_Muschelkalk.gml, InSpEE_DS_GeologicUnit_Salt_distribution_in_Germany_Roet.gml, InSpEE_DS_GeologicUnit_Salt_distribution_in_Germany_Zechstein.gml and InSpEE_DS_GeologicUnit_Salt_distribution_in_Germany_Rotliegend.gml represent the salt distribution of the respective stratigraphic unit. InSpEE_DS_GeologicUnit_General_salt_distribution.gml represents the general salt distribution in Germany. This geographic information is product of a BMWi-funded research project "InSpEE-DS" running from the year 2015 to 2019. The acronym stands for "Information system salt: planning basis, selection criteria and estimation of the potential for the construction of salt caverns for the storage of renewable energies (hydrogen and compressed air) - double saline and flat salt layers".
-

Which salt formations are suitable for storing hydrogen or compressed air? In the InSpEE-DS research project, scientists developed requirements and criteria for the assessment of suitable sites even if their exploration is still at an early stage and there is little knowledge of the salinaries’ structures. Scientists at DEEP.KBB GmbH in Hanover, worked together with their project partners at BGR and the Leibniz University Hanover, Institute for Geotechnics, to develop the planning basis for the site selection and for the construction of storage caverns in flat layered salt and multiple or double saliniferous formations. Such caverns could store renewable energy in the form of hydrogen or compressed air. While the previous project InSpEE was limited to salt formations of great thickness in Northern Germany, salt horizons of different ages have now been examined all over Germany. To estimate the potential, depth contour maps of the top and the base as well as thickness maps of the respective stratigraphic units were developed. Due to the present INSPIRE geological data model, it was necessary, in contrast to the original dataset, to classify the boundary lines of the potential storage areas in the Zechstein base and thickness layers, whereby the classification of these lines was taken from the top Zechstein layer. Consequently, the boundary element Depth criterion 2000 m (Teufe-Kriterium 2000 m) corresponds on each level to the 2000 m depth of Top Zechstein. However, the boundary of national borders and the boundary of the data basis could not be implemented in the data model and are therefore not included in the dataset. Information on compressed air and hydrogen storage potential is given for the identified areas and for the individual federal states. According to the Data Specification on Geology (D2.8.II.4_v3.0) the content of InSpEE-DS (INSPIRE) is stored in 18 INSPIRE-compliant GML files: InSpEE_DS_GeologicUnit_Isopachs_Zechstein.gml contains the Zechstein isopachs. InSpEE_DS_GeologicUnit_Isobaths_Top_Zechstein.gml and InSpEE_DS_GeologicUnit_Isobaths_Basis_Zechstein.gml contain the isobaths of the top and basis of Zechstein. The three files InSpEE_DS_GeologicStructure_ThicknessMap_Zechstein, InSpEE_DS_GeologicStructure_Top_Zechstein and InSpEE_DS_GeologicStructure_Basis_Zechstein represent the faults of the Zechstein body as well as at the top and at the basis of the Zechstein body. InSpEE_DS_GeologicUnit_Boundary_element_Potential_areas_Zechstein.gml contains the boundary elments of the potential areas at the top and the basis of Zechstein as well as of the Zechstein body. The three files InSpEE_DS_GeologicUnit_Uncertainty_areas_ThicknessMap_Zechstein.gml, InSpEE_DS_GeologicUnit_Uncertainty_areas_Top_Zechstein.gml, InSpEE_DS_GeologicUnit_Uncertainty_areas_Basis_Zechstein.gml represent the uncertainty areas of the Zechstein body as well as at the top and at the basis of the Zechstein body. InSpEE_DS_GeologicUnit_Potentially_usable_storage_areas_Storage_potential_in_the_federal_states.gml comprises the areas with storage potential for renewable energy in the form of hydrogen and compressed air. The six files InSpEE_DS_GeologicUnit_Salt_distribution_in_Germany_Malm.gml, InSpEE_DS_GeologicUnit_Salt_distribution_in_Germany_Keuper.gml, InSpEE_DS_GeologicUnit_Salt_distribution_in_Germany_Muschelkalk.gml, InSpEE_DS_GeologicUnit_Salt_distribution_in_Germany_Roet.gml, InSpEE_DS_GeologicUnit_Salt_distribution_in_Germany_Zechstein.gml and InSpEE_DS_GeologicUnit_Salt_distribution_in_Germany_Rotliegend.gml represent the salt distribution of the respective stratigraphic unit. InSpEE_DS_GeologicUnit_General_salt_distribution.gml represents the general salt distribution in Germany. This geographic information is product of a BMWi-funded research project "InSpEE-DS" running from the year 2015 to 2019. The acronym stands for "Information system salt: planning basis, selection criteria and estimation of the potential for the construction of salt caverns for the storage of renewable energies (hydrogen and compressed air) - double saline and flat salt layers".
-
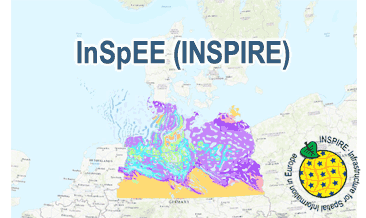
The WMS InSpEE (INSPIRE) provides information about the areal distribution of salt structures (salt domes and salt pillows) in Northern Germany. Contours of the salt structures can be displayed at horizontal cross-sections at four different depths up to a maximum depth of 2000 m below NN. The geodata have resulted from a BMWi-funded research project “InSpEE” running from the year 2012 to 2015. The acronym stands for "Information system salt structures: planning basis, selection criteria and estimation of the potential for the construction of salt caverns for the storage of renewable energies (hydrogen and compressed air)”. Taking into account the fact that this work was undertaken at a scale for providing an overview and not for investigation of single structures, the scale of display is limited to a minimum of 1:300.000. Additionally four horizontal cross-section maps display the stratigraphical situation at a given depth. In concurrence of maps at different depths areal bedding conditions can be determined, e.g. to generally assess and interpret the spread of different stratigraphic units. Clearly visible are extent and shape of the salt structures within their regional context at the different depths, with extent and boundary of the salt structures having been the main focus of the project. Four horizontal cross-section maps covering the whole onshore area of Northern Germany have been developed at a scale of 1:500.000. The maps cover the depths of -500, -1000, -1500, -2000 m below NN. The four depths are based on typical depth requirements of existing salt caverns in Northern Germany, mainly related to hydrocarbon storage. The shapes of the structures show rudimentary information of their geometry and their change with depths. In addition they form the starting point for rock mechanical calculations necessary for the planning and construction of salt caverns for storage as well as for assessing storage potentials. The maps can be used as a pre-selection tool for subsurface uses. It can also be used to assess coverage and extension of salt structures. Offshore areas were not treated within the project. All horizontal cross-section maps were adjusted with the respective state geological survey organisations. According to the Data Specification on Geology (D2.8.II.4_v3.0) the WMS InSpEE (INSPIRE) provides INSPIRE-compliant data. The WMS InSpEE (INSPIRE) contains two group layers: The first group layer “INSPIRE: Salt structures in Northern Germany“ comprises the layers GE.Geologic.Unit.Salt structure types, GE.GeologicUnit.Salt pillow remnants, GE.GeologicUnit.Structure-building salinar and GE.GeologicUnit.Structural outlines. The layer GE.GeologicUnit.Structural outlines contains according to the four depths four sublayers, e.g. GE.GeologiUnit.Structural outlines 500 m below NN. The second group layer „INSPIRE: Horizontal cross-section maps of Northern Germany“ comprises according to the four depths four layers, e.g. Horizontal cross-section map – 500 m below NN. This layer, in turns, contains two sublayers: GE.GeologicFault.Relevant fault traces and GE.GeologicUnit.Stratigraphic Units. Via the getFeatureInfo request the user obtains additional information on the different geometries. In case of the GE.Geologic.Unit.Salt structure types the user gets access to a data sheet with additional information and further reading in German for the respective salt structure via the getFeatureInfo request.
-

InSpEE (INSPIRE) provides information about the areal distribution of salt structures (salt domes and salt pillows) in Northern Germany. Contours of the salt structures can be displayed at horizontal cross-sections at four different depths up to a maximum depth of 2000 m below NN. The geodata have resulted from a BMWi-funded research project “InSpEE” running from the year 2012 to 2015. The acronym stands for "Information system salt structures: planning basis, selection criteria and estimation of the potential for the construction of salt caverns for the storage of renewable energies (hydrogen and compressed air)”. Additionally four horizontal cross-section maps display the stratigraphical situation at a given depth. In concurrence of maps at different depths areal bedding conditions can be determined, e.g. to generally assess and interpret the spread of different stratigraphic units. Clearly visible are extent and shape of the salt structures within their regional context at the different depths, with extent and boundary of the salt structures having been the main focus of the project. Four horizontal cross-section maps covering the whole onshore area of Northern Germany have been developed at a scale of 1:500.000. The maps cover the depths of -500, -1000, -1500, -2000 m below NN. The four depths are based on typical depth requirements of existing salt caverns in Northern Germany, mainly related to hydrocarbon storage. The shapes of the structures show rudimentary information of their geometry and their change with depths. In addition they form the starting point for rock mechanical calculations necessary for the planning and construction of salt caverns for storage as well as for assessing storage potentials. The maps can be used as a pre-selection tool for subsurface uses. It can also be used to assess coverage and extension of salt structures. Offshore areas were not treated within the project. All horizontal cross-section maps were adjusted with the respective state geological survey organisations. According to the Data Specification on Geology (D2.8.II.4_v3.0) the content of InSpEE (INSPIRE) is stored in 15 INSPIRE-compliant GML files: InSpEE_GeologicUnit_Salt_structure_types.gml contains the salt structure types (salt domes and salt pillows), InSpEE_GeologicUnit_Salt_pillow_remnants.gml comprises the salt pillow remnants, InSpEE_GeologicUnit_Structure_building_salinar.gml represents the structural salinar(s), the four files InSpEE_Structural_outlines_500.gml, InSpEE_Structural_outlines_1000.gml, InSpEE_Structural_outlines_1500.gml and InSpEE_Structural_outlines_2000.gml represent the structural outlines in the corresponding horizontal cross-sections, the four files InSpEE_GeologicUnit_Cross_Section_500, InSpEE_GeologicUnit_Cross_Section_1000, InSpEE_GeologicUnit_Cross_Section_1500 and InSpEE_GeologicUnit_Cross_Section_2000 display the stratigraphical situation in the corresponding horizontal cross-sections and the four files InSpEE_GeologicStructure_500.gml, InSpEE_GeologicStructure_1000.gml, InSpEE_GeologicStructure_1500.gml and InSpEE_GeologicStructure_2000.gml comprise the relevant fault traces in the corresponding horizontal cross-sections. The GML files together with a Readme.txt file are provided in ZIP format (InSpEE-INSPIRE.zip). The Readme.text file (German/English) contains detailed information on the GML files content. Data transformation was proceeded by using the INSPIRE Solution Pack for FME according to the INSPIRE requirements.
-
Depth maps for the layers of the Zechstein to the seafloor surface were taken from the generalized structural model of the central German North Sea sector (GSN). The GSN is based on the data of the Geotectonic Atlas (Baldschuhn et al., 2001) in the area of the central German North Sea. They were recompiled within the GPDN project to create a KW model and revised to meet the demands of numerical basin modeling. The aim of the 3D numerical modeling is to reconstruct the subsidence, temperature and maturation history of carboniferous petroleum source rocks, which can be used as a basis for estimating the KW potential. To create the maps, depth and thickness information from the printed maps was converted to a contiguous surface by scanning, georeferencing, digitizing isolines, and interpolation. Simplification and correction was used for modeling, especially in overlap areas and below salt diapirs and in large fault zones. The maps are available for download in two different data formats (CPS3 and Zmap). The individual depth maps have a file size of 8.5 MB each (zip files 0.3 to 1.3 MB).
-
The initial thickness of a sedimentary layer was determined for the Jurassic and Triassic strata by own estimations from the missing thicknesses in the area of the salt domes and from calibrated 1D models. In addition, a comparison was made with literature data from Doornebal et al. 2010 (SPBA), DGMK 2010, Maystrenko 2013. The initial thickness maps for the Carboniferous Stefan and Westfal horizons were taken from Krull (2005). For this purpose, the printed maps were converted into a contiguous surface by scanning, georeferencing, digitizing the isolines, and interpolation. The maps are available for download in two different data formats (CPS3 and Zmap). The individual thickness maps have a file size of 8.5 MB each (zip files 0.3 to 1.4 MB). The initial thickness maps were produced for the Carboniferous, Triassic and Jurassic sedimentary units. These maps form the basis for the erosion maps of the input model.
-
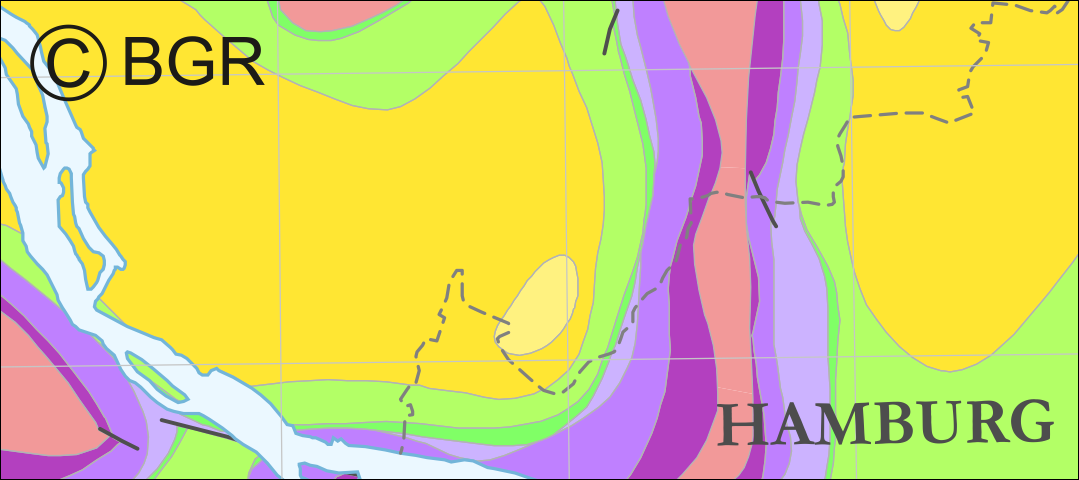
Horizontal cross-section maps display the geological situation at a given depth. In concurrence of maps at different depths areal bedding conditions can be determined, e.g. to generally assess and interpret the spread of different stratigraphic units. Clearly visible are extent and shape of the salt structures within their regional context at the different depths, with extent and boundary of the salt structures having been the main focus of the project. Four horizontal cross-section maps covering the whole onshore area of Northern Germany have been developed at a scale of 1:500.000. The maps cover the depths of -500, -1000, -1500, -2000 m below NN. The four depths were selected by the project partners and are based on typical depth requirements of existing salt caverns in Northern Germany, mainly related to hydrocarbon storage. The shapes of the structures show rudimentary information of their geometry and their change with depths. In addition they form the starting point for rock mechanical calculations necessary for the planning and construction of salt caverns for storage as well as for assessing storage potentials. The maps can be used as a pre-selection tool for subsurface uses. It can also be used to assess coverage and extension of salt structures. As, at the time of preparation of the maps, energy storage and cavern operation in offshore areas could not be assumed as a priority, such areas were not treated within the project. All horizontal cross-section maps were adjusted with the respective state geological survey organisations.
-
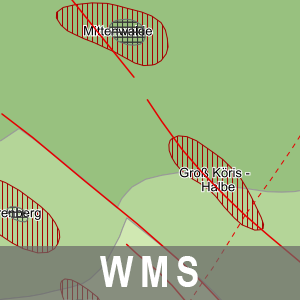
Der Darstellungsdienst (WMS) Strukturgeologische Übersicht Brandenburg stellt Daten zur Strukturgeologische Übersicht bereit. Dieser wird dominiert durch die NW-SE streichende intrakratonale Norddeutsche Senke, deren Basis sich im nördlichen und mittleren Teil des Landesterritoriums auf über 5 000 m Tiefe absenkt und nach Süden und Südosten heraushebt. Das Beckenzentrum setzt sich von Nordwest-Brandenburg in Richtung Unterelbe fort. Dagegen ist die jetzige südliche Begrenzung tektonisch bedingt. Die strukturgeologischen Verhältnisse werden durch die jetzige Tiefenlage der Zechsteinbasis und die strukturelle Modulierung der Zechsteinoberfläche wiedergegeben. Weitere Informationen unter: https://geo.brandenburg.de/karten/htdocs/salinar.pdf. Die Strukturgeologische Übersicht Brandenburg gehört thematisch zu der Rohstoff- und Tiefengeologie. Diesem Thema sind zwei weitere Dienstethemen zugeorndet: - WMS/WFS/WCS Reflexionsseismische Horizonte 2D BB, - WMS/WFS Karte der oberflächennahen Rohstoffe 1: 50 000 BB. Der WMS beinhaltet die folgenden Layer: - Beschriftungen Störungen [bstoerungen], - Beschriftungen Blöcke [bbloecke], - Störungen [stoer], - Diapir [diapir], - Kissen [kissen], - Zechstein [zechstein].
-
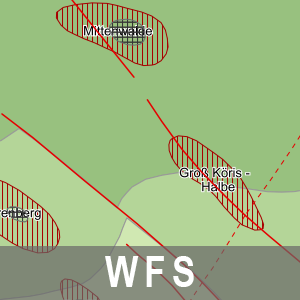
Der Downloaddienst (WFS) Strukturgeologische Übersicht Brandenburg stellt Daten zur Strukturgeologische Übersicht bereit. Dieser wird dominiert durch die NW-SE streichende intrakratonale Norddeutsche Senke, deren Basis sich im nördlichen und mittleren Teil des Landesterritoriums auf über 5 000 m Tiefe absenkt und nach Süden und Südosten heraushebt. Das Beckenzentrum setzt sich von Nordwest-Brandenburg in Richtung Unterelbe fort. Dagegen ist die jetzige südliche Begrenzung tektonisch bedingt. Die strukturgeologischen Verhältnisse werden durch die jetzige Tiefenlage der Zechsteinbasis und die strukturelle Modulierung der Zechsteinoberfläche wiedergegeben. Weitere Informationen unter: https://geo.brandenburg.de/karten/htdocs/salinar.pdf. Die Strukturgeologische Übersicht Brandenburg gehört thematisch zu der Rohstoff- und Tiefengeologie. Diesem Thema sind zwei weitere Dienstethemen zugeorndet: - WMS/WFS/WCS Reflexionsseismische Horizonte 2D BB, - WMS/WFS Karte der oberflächennahen Rohstoffe 1: 50 000 BB. Der WFS beinhaltet die folgenden FeatureTypes: - Störungen [app:stoer], - Diapir [app:diapir], - Kissen [app:kissen], - Zechstein [app:zechstein].
-
Der Band Nr. 6 aus der Publikationsreihe „Fortschritte in der Geologie von Rheinland und Westfalen“ befasst sich mit den Sedimentabfolgen des Tertiärs, Juras, Zechsteins, Karbons und Devons im Bereich der Niederrheinischen Bucht. [1962. 462 S., 53 Abb., 14 Tab., 59 Taf.; ISBN 978-3-86029-820-6]
 www.geodatenkatalog.de (S1L)
www.geodatenkatalog.de (S1L)