Keyword
forest
6 record(s)
Provided by
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Update frequencies
Service types
-
-

The Tree Species Germany product provides a map of dominant tree species across Germany for the year 2022 at a spatial resolution of 10 meters. The map depicts the distribution of ten tree species groups derived from multi-temporal optical Sentinel-2 data, radar data from Sentinel-1, and a digital elevation model. The input features explicitly incorporate phenological information to capture seasonal vegetation dynamics relevant for species discrimination. A total of over 80,000 training and test samples were compiled from publicly accessible sources, including urban tree inventories, Google Earth Pro, Google Street View, and field observations. The final classification was generated using an XGBoost machine learning algorithm. The Tree Species Germany product achieves an overall F1-score of 0.89. For the dominant species pine, spruce, beech, and oak, class-wise F1-scores range from 0.76 to 0.98, while F1-scores for other widespread species such as birch, alder, larch, Douglas fir, and fir range from 0.88 to 0.96. The product provides a consistent, high-resolution, and up-to-date representation of tree species distribution across Germany. Its transferable, cost-efficient, and repeatable methodology enables reliable large-scale forest monitoring and offers a valuable basis for assessing spatial patterns and temporal changes in forest composition in the context of ongoing climatic and environmental dynamics.
-
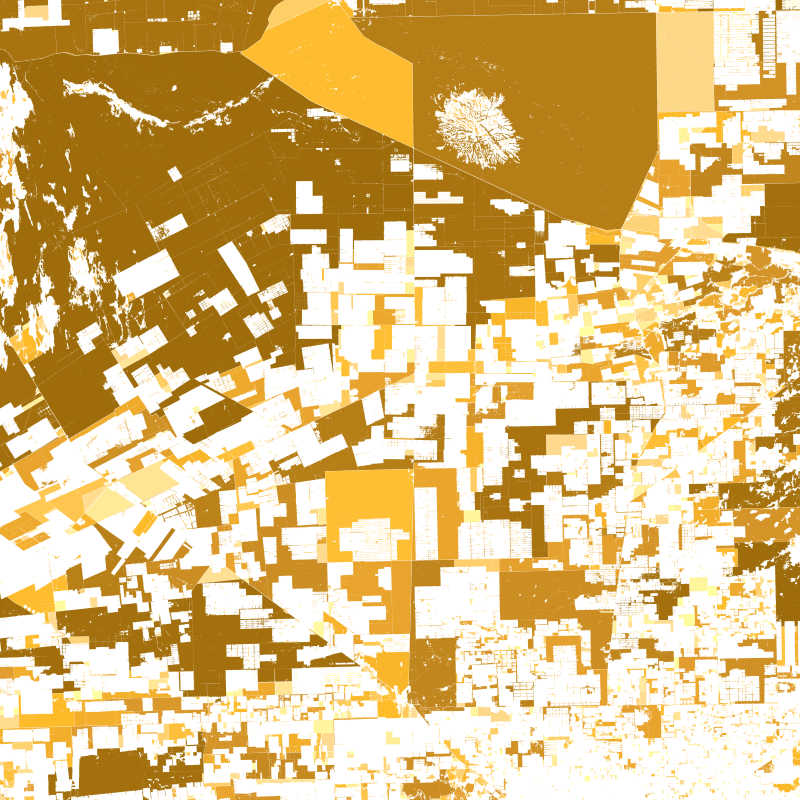

This product is a shape file of all detected forest patches in the Paraguayan Chaco that are larger than 10 hectars fort he years 2000, 2010, and 2020. Every forest patch contains information on its perimeter, size, shape, and core area. By looking at all forest patches together, an impression can be gained of the fragmentation of the forest in the Paraguayan Chaco. Proximity is a measure of fragmentation. Areas of large and close by forest patches show high proximity values while isolated patches or patchest hat are only surrounded by small forest patches, have a small proximity. The Core area index quantifies the share of core area in the entire forest patch area. Thereby, corea area is the area of a forest patch with at least 500m distance to the edge of the forest. The Shape index is calculated from perimeter and area of a patch. The fragementation of a forest often has the effect that the ratio between area and perimeter is affected. The edge lengths become longer while the surface area becomes smaller.
-

-
-
 www.geodatenkatalog.de (S3L)
www.geodatenkatalog.de (S3L)