Contact for the resource
Federal Institute for Geosciences and Natural Resources
79 record(s)
Provided by
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Service types
-
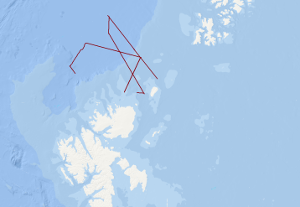
The research cruise PANORAMA-1 onboard the Italian vessel OGS Explora was carried out within 2 legs in the period August, 16th – September 17th 2013. The designated survey area was located in a sector of the European Arctic north of Svalbard covering an area north of 80°N between 15°E and 35°E. Main objectives were to acquire new geophysical data and extract near surface sediment samples in an underexplored area of the European Arctic with special focus on the transition zone from the North Barents shelf towards the oceanic Nansen basin. During leg 1 of the cruise a 20 days geophysical survey 1056 km of multi-channel seismic data was acquired supplemented by a 221 km long sonobuoy profile. Additionally, magnetic and sediment echosounding data was acquired along these profiles. During all operations within the survey area gravity and multibeam echosounding data was continuously acquired. After a 1 day stopover in Longyearbyen in order to exchange part of the scientific crew OGS Explora returned to the survey area to continue survey operations during leg 2. Within these 10 days period near surface sediments were extracted by means of a gravity corer at 12 locations and heat flow soundings were conducted at 7 locations. Gravity, sediment and multibeam echosounding data was continuously acquired along all transit lines within the survey area during leg 2. Total line length of magnetic data was 2658.7 km. Over all track lines with bathymetric and gravity data amount to 5665.8 km in total.
-
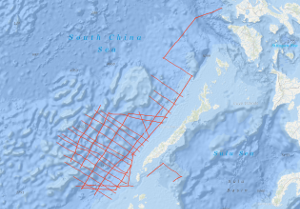
As recommended by the Joint CCOP-IOC Working Group on Post-IDOE Studies on East Asia Tectonics and Resources and the proposal of the Bureau of Mines and Geosciences of the Philippines to extend the research of the previous R/V SONNE survey SO-23, the Federal Institute of Geosciences and Natural Resources (BGR) carried out a geophysical survey in the southeastern part of the South China Sea (Dangerous Grounds) and in the northwestern part of the Sulu Sea in two legs from 29th April to 29th June 1983 on SONNE cruise SO-27. Multichannel reflection seismic measurements were carried out in parallel with magnetic, gravimetric, Sea-Beam, and 3.5 kHz subbottom profiler measurements on 34 lines with a total length of 7,204 km. In addition, 26 lines with a total length of 2,800 km were surveyed with only the last four named methods. SONNE cruise SO-27 was financed by the Federal Ministry of Research and Technology (BMFT). Six seismic sequences (DG-1 to DG-6) (DG = Dangerous Grounds) could be distinguished in the surveyed part of the South China Sea. The oldest recognizable sequence is the sequence DG-6, an equivalent of the Pre-Nido Formation of the northwest shelf of Palawan. Seismic unconformity Violet marks the top of the DG-6 sequence, which consists of a complex system of tilted horsts and half-grabens. The half-grabens are presumably filled with clastic sediments of Eocene age (seismic sequence DG-5). The top of seismic sequence DG-5 is bounded by unconformity Blue, which is interpreted as representing the end of the rift phase and the onset of seafloor spreading in the South China Sea about 32 m.y. ago. The overlying seismic sequence DG-4 is characterized by an internal reflection pattern with low frequencies. Lithologically, this sequence consists of shallow-water carbonates with reef complexes of Oligocene to Early Miocene age and has to be regarded as equivalent to the oil-containing Nido Formation of the Palawan shelf. A rapid subsidence of large parts of the survey area during the late (?) Early Miocene ended the growth of the shallow water carbonate platform, indicated by the unconformity Blue. The overlying seismic sequence DG-3 is interpreted as consisting of a transitional facies between a shallow water and a bathyal depositional environment. The top of this sequence is marked by unconformity Red, which most probably represents the end of the drifting phase (seafloor spreading) in the South China Sea during the Middle Miocene. The most prominent structural feature of the shelf and slope of central and southern Palawan is a thick sedimentary wedge originally interpreted as a melange. Our data show that the Oligocene to Early Miocene carbonate platform of the Dangerous Grounds extends beneath the Palawan Trough, as well as beneath the central and southern Palawan shelf, underlying the melange. Based on the finding that i) Rhaeto-Liassic rocks are present in the Dangerous Grounds, ii) the Oligocene to Early Miocene carbonate platform continues from the Dangerous Grounds through the Palawan Trough to the central and southern Palawan shelf, and iii) there is thinned continental crust 20 km thick below the continental slope of southern Palawan, we believe the Dangerous Grounds, together with Palawan and the Caiman Islands belong to a uniform continental fragment which separated from the proto-chinese continental margin when the South China Sea opened during the Oligocene. Previously, the melange of central and southern Palawan, which contains ophiolites, was interpreted as being autochthonous. In our opinion, the melange is an allochthonous mass which has been overthrusted onto the eastern margin of the Dangerous Grounds-Palawan-Caiman microcontinent from the Northwest Sulu Basin. The Ulugan Bay fault is interpreted as the northeastern front of this allochthonous mass. The area of prospective carbonate plays is considerably enlarged by the discovery that the Oligocene to Early Miocene carbonate platform with Nido-type reef structures extends below the allochthonous sediments of central and southern Palawan. We expect that hydrocarbon-bearing structures of the Sabah-type, i. e. thick, folded Neogene sediments, will be found in the western part of the northwestern Sulu basin. If our interpretation is correct, a new chapter of hydrocarbon exploration may be about to begin around Palawan in the Philippines.
-
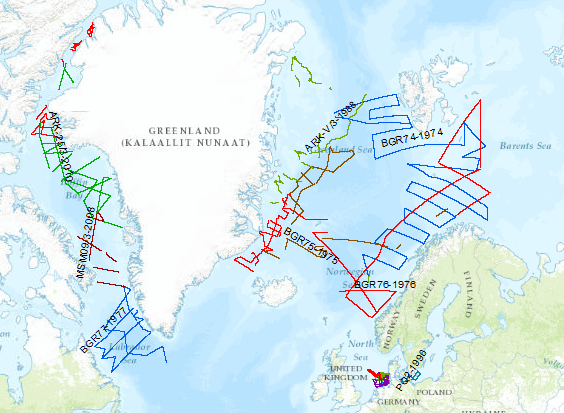
During the period from 1974 to 2023 various cruises from BGR acquired seismic lines worldwide. The aim of these marine expeditions were a detailed survey of the geological structure of seabed.
-
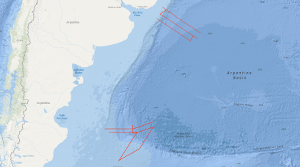
From 19th November to 19th December 2004 BGR conducted a marine geophysical cruise between 34°S and 36°S off Uruguay and between 46°S and 50°S off Argentine. The main research objective was to contribute to a better understanding of the initial breakup and the early opening of the South Atlantic. In continuation of our former work on the South Atlantic continental margins off Argentina, Brazil, Uruguay, Namibia and South Africa marine geophysical research (multi-channel seismics, refraction-/wide-angle reflection seismics, magnetics and gravity) was performed in close cooperation with the Argentine and Uruguayan authorities Comisión Nacional del Límite Exterior de la Plataforma Continental (COPLA) of Argentina and Servicio de Oceanograficia, Hidrograficia y Meteorologia de la Armada (SOHMA) of Uruguay. Multi-channel seismic lines with a total length of 3,754 km and additional 3540 km with the other geophysical methods were acquired . Along two lines refraction-/wide-angle reflection seismic work was carried out. The preliminary analyses of the new seismic data show different images of the crustal structures between Uruguay and southern Argentine with regard to the distribution and volume of offshore volcanic rocks (seaward dipping reflector sequences, SDRS) along the South American Atlantic margin. On the northern profiles between 34°S and 36°S one single well developed wedge of SDRS is present. Although the landward termination (‘feather edge’) on most of the lines is masked by multiples the average total width of the wedge across the margin seems to be 90 – 100 km and is very constant for this margin segment. This is strong contrast to the results from former cruises (BGR87, SO85 and BGR98) which covered the area between 38°S and 45°S. There, the SDRS showed distinct multiple wedges which in some places extend over 120 km across the continental slope. The investigation of the sedimentary section yielded that in the area off Uruguay widespread bottom simulating reflectors (BSR) are present. This indications for stable gas hydrates cover a total area of 7000 km2. One major aim of the cruise was to cover the transition between a volcanic passive margin and a non-volcanic passive resp. sheared margin. This was accomplished in the southern part of the investigated area. Two EW-trending profiles across the Argentine shelf into the Argentine Basin still show indications for SDRS but these structures are only 25 – 30 km wide. The profiles which extend from the NE to the SW crossing the Agulhas-Falkland Fracture Zone (AFFZ) onto the Falkland Plateau show the typical trend of a sheared margin. At the northern rim of the Falkland Plateau a set of small pre-rift half grabens were found indicating pre-rift extensional tectonic phases. The magnetic data in the area off Uruguay show lineations which are preliminary interpreted as chrons M0 to M3. This might indicate that the first (oldest) oceanic crust was created at a time around the magnetic polarity reversal between the normal interval M4 and the reversed interval M3 (126-127 Ma). Together with existing data from previous cruises this indicates that the breakup of the South Atlantic started further South because there magnetic chrons back to M9 (130 Ma) were identified. In the southernmost part of the margin at 47°S only the magnetic lineations M0 to M4 were identified in the oceanic domain Nevertheless, it is likely that between M4 and the assumed position of the continent ocean boundary/transition (COB/COT) older oceanic crust exists that for some reasons does not show correlatable lineations. The the free-air gravity map is dominated by the main topographic and structural features in the survey area. Rifted continental margins are characterized by prominent free-air gravity anomalies elongated parallel to the ocean-continent transition. The continental slope is considerably steeper in the North off Uruguay than in the South and thus the gravity high is much more pronounced in the North than in the South. The simple Bouguer anomaly map also shows the difference between the more gentle and wider continental slope in the South and the steeper slope in the North. The lowest Bouguer gravity values are found in the area of the basins on the continental shelf. Especially the Salado Basin in the prolongation of the Rio de la Plata and the Colorado Basin at about 40°S are indicated by Bouguer gravity anomaly highs. The interpretation by forward density modelling shows, however, the presence of SDRS units in the North of relative high density in the area of the continental slope. Whereas the modelling shows no indications for such volcanic bodies in the South. Although the MCS data indicate a small SDRS wedge but this body may be too small to cause an anomaly.From 17th April to 6th June 2003 BGR conducted a marine geophysical cruise between 30°S and 38°S off the Atlantic coast of South Africa. The main research objective was to contribute to a better understanding of the initial breakup and the early opening of the South Atlantic. In continuation of our former work on the South Atlantic continental margins off Argentina, Brazil, Uruguay and Namibia marine geophysical research (multi-channel seismics, wide-angle refraction seismics, magnetics and gravity) was performed in cooperation with the Petroleum Agency South Africa (PASA). Multi-channel lines with a total lenght of 3,260 km, and additional 1,365km, with the other geophysical methods were acquired. Combined onshore/offshore refraction seismic work in cooperation with GeoForschungsZentrum Potsdam (Germany) and the Council for Geoscience (South Africa) was also part of the program.
-
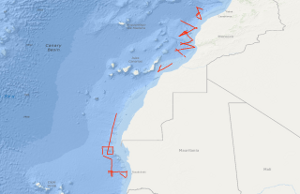
In the period from September 25th to October 19th 1979 5,260 km of magnetic, gravity and bathymetric lines and 3,567 km of reflection seismic lines were recovered on the first leg of the VALDIVIA Westafrica-cruise 1979 with the research objective to study similarities and differences in the geological development of physiographically different Northwest African continental margin segments. Test measurements have been carried out during this cruise with an “implosive" seismic sound source. The software for acquisition, calculation and presentation of gravity, magnetic and bathymetric data has been developed so that onboard presentation of free-air anomalies, Bouguer anomalies, anomalies of the earth's magnetic field and of the bathymetry could be achieved. Differences within the regional geological development of the Northwest African continental margin has been confirmed. Parts of the Moroccan continental margin are modified by a Cretaceous epirogenic uplift associated with block—faulting and halokinesis. Tertiary folding of the Western High Atlas extends into the shelf of the Tafelney Plateau segment.
-
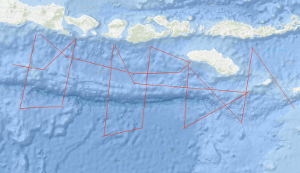
Within the framework of the research project SINDBAD (Seismic and Geoacoustic Investigations Along the Sunda-Banda Arc Transition) marine geophysical investigations have been carried out with RV SONNE from October 9th, 2006, to November 9th, 2006, off the eastern Sunda Arc and at the transition to the Banda Arc in Indonesia. The research cruise SO190 Leg 1 started in Jakarta, Indonesia and ended in Darwin, Australia. During this cruise, multichannel seismics (MCS), magnetics (M), and gravimetry (G) measurements have been carried out. Simultaneously, SIMRAD (multibeam echosounder) and PARASOUND (sediment echosounder) data have been collected using RV SONNEs onboard systems. During the expedition, a total of 4,933 km of profiles with MCS, M, and G have been acquired. Six of the 20 profiles are long overview profiles perpendicular to the deformation front and cover the entire forearc from the forearc basin across the outer arc high, the deformation front onto the oceanic lithosphere. Additional profiles have been acquired along strike in the Lombok forearc basin and in the Savu Basin. The main goal of the project SINDBAD is to investigate the relation between the variability of the lower plate and the tectonic evolution of the overriding plate (formation of an outer arc high, development of forearc basins, and accretion and erosion processes of the overriding plate). The "raw materials" – seafloor sediments, oceanic crust (at the Banda Arc also continental crust) and mantle lithosphere – are carried into the subduction system at the trench. The influence of these "raw materials" on the overriding plate is controlled by a number of factors: e.g. the convergence rate, the obliqueness of convergence and the physical and chemical properties of the lower plate (e.g. its age, its sediment-cover and –thickness, its fluid content and the composition of the crust). Forearc basins are today attracting increased attention because of their hydrocarbon potential. The forearc basins of the eastern Sunda Arc are still frontier areas which are almost unexplored. An additional goal of this project is therefore the assessment of the hydrocarbon potential of the Lombok Basin. In contrast to the Sumatra subduction zone, only a small amount of pelagic sediment is carried into the subduction system offshore East Java, Bali, Lombok, Sumbawa and Sumba. This results e.g. in a less pronounced development of the outer arc high, which is subaerial off Sumatra, but entirely below the sea surface in the eastern Sunda Arc. The Roo Rise, which is subducting off East Java, is a morphological high that lies about 1500 m higher than the Argo Abyssal Plain which is subducting further to the east. Despite of these pronounced differences, the deformation front in both areas shows similarities. While the foot of the slope shows lower dip than the upper slope, both areas are characterized by landward dipping thrust sheets. In both areas the outer arc high is characterized by active faults (the recent activity is indicated by deformed basin sediments on the outer arc high) and therefore no indications for a static backstop have been found. The accretionary character of the deformation front is clearly indicated in both areas, while subrosion in association with the subsidence of the Lombok Basin can not be excluded based on the preliminary interpretations. The trench in both areas is devoid of sediments, which indicates erosional processes caused by currents along the trench strike. However, a depocenter for these sediments could not be localized yet. While a forearc basin is not clearly developed off East Java, the Lombok forearc basin with water depths of more than 4000 m extends from off Bali to off Sumbawa. On the southern slope of the basin prograding sedimentary sequences indicate uplift, probably caused by the subducting Roo Rise or a growth of the outer arc high. Additionally, carbonate platforms on the acoustic basement indicate phases of rapid subsidence of the basin. The sediment thickness reaches a total of about 3.5 sec TWT. A few seismic "bright spots", but no bottom simulating reflectors (BSRs) have been identified in the basin. The profiles striking along the basin axis indicate paleo-depocenters in the western part of the profile, while the recent depocenter is located in the eastern part of the basin. On the northern flank of the Lombok basin, indications for submarine volcanism (recent activity is unknown) are indicated by a seamount reaching above the seafloor associated with a clear magnetic anomaly. East of the Lombok Basin the island of Sumba is located, which is regarded as a microcontinent that has been attached to the island arc during the Late Oligocene. Sumbas geographical location in front of the island arc is usually characterized by the location of a forearc basin and correlates with the seaward displacement of the deformation front (Roti Basin) at the transition from ocean/island arc subduction of the Sunda Arc to continent/island arc collision of the Banda Arc. An uplift of about 0.5 cm/a is reported for Sumba, associated with the underplating of the continental Scott Plateau. The uplift is especially evident in the MCS data. To the east of the Lombok Basin depocenter, a transition zone with deep reaching faults is observed, associated with eastward dipping sedimentary and basement structures. This transition zone is also indicated by anomalies in the magnetic and gravity data, the latter indicating isostatic undercompensation. On the western flank of Sumba, deformed sedimentary sequences indicate gravitational gliding in association with the uplift of Sumba. East of Sumba, two profiles into the Savu Basin have been acquired. Here the uplift of Sumba is indicated by the erosion of sedimentary sequences which have been deposited in the basin followed by uplift and subsequent erosion. Further indications of "inversion structures" are given by a reactivated thrust fault that in the past has served as the southern boundary of the Savu Basin und indicates recent activity by associated deformed basin sediments. The oceanic crust of the Argo Abyssal Plain and the Roo Rise is characterized by thin sediments. On a connection profile between two long profiles on the Argo Abyssal Plain a basin with about 1.4 sec TWT of sediment has been observed, that, indicated by a magnetic anomaly, can be correlated with an age jump of about 15 Ma, thereby indicating a paleo plate boundary.
-
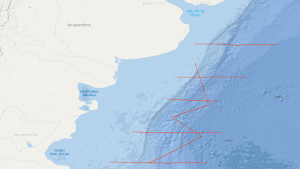
In the period from 22nd December, 1987 to 15th January, 1988 a geophysical reconnaissance survey has been carried out with S.V. EXPLORA on the Argentine Eastern continental margin. A total of 3,675 km of digital seismic reflection profiles in parallel with gravimetric and in part magnetic measurements, and 13 sonobuoy refraction profiles were recorded during this survey. The general aim of the survey was to search the Argentine eastern continental margin between 37°S and 47°S for evidence of continent-ocean boundary structures previously recognized by us off South Africa. The following preliminary results were obtained: (1) Five regional seismic markers/unconformities have been observed, named from bottom to top AR V to AR I. (2) Two units are recognizable on all reflection seismic records: A buried lower unit the top of which is marked by the distinct 'AR IV' unconformity of presumably Beriasian/Valangian age, and a tectonically undisturbed upper sedimentary unit. (3) The dominant feature of the lower unit is a 50 km to 100 km broad wedge-shaped body characterized by an internally divergent pattern of reflection horizons having seaward dip. The seismic characteristics and recent ODP drilling is consistent with the wedge being formed from extrusive basaltic rocks. (4) The more than 5000 m thick wedge is parallel with the shelf edge and can be traced continuously for 1200 km. Its landward pinchout coincides with the magnetic slope anomaly 'G'. (5) A giant contourite mound of Neogene age has been recognized in the southeastern part of the survey area. (6) Bottom simulating reflectors have been recognized. Their occurrence is associated with the contourite mound.
-
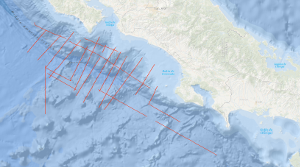
The structure and tectonics of the Pacific margin of Costa Rica were studied by multichannel seismic measurements in parallel with gravity measurements and swathmapping from the Cocos Ridge to Nicoya Peninsula during R/V SONNE cruise SO81 legs 1 and 2 from 18th August to 15th September 1992. In addition geological sampling has been carried out. Dominant structural feature is the buried Costa Rica Terrrane (CRT), a complex and segmented, wedge-shaped unit characterized by relative high seismic velocities of 4 km/s. The thickness of this several tens of kilometres wide zone varies between 0.5 and 3 s (twt). The CRT forms the backstop against which the sediments of the subducting Cocos plate accrete resulting in accumulation of sedimentary mass beneath and in front of the CRT, as well as in simultaneous uplift and fracturing of the CRT. It appears that the distinct CRT is affected locally by raft tectonics, i.e. a form of thin-skinned extension by normal faulting from gravity sliding over a non-stretched oceanic crust. A unit is recognizable between the base of the CRT and the surface of the subducting oceanic crust on most of the seismic lines. This unit is thought to consist mostly of ductile pelagic to hemipelagic shales. Some segment boundaries of the CRT are associated with morphological furrows, 5 to 10 km wide and up to 30 km long running across the slope. We feel that the data acquired during SONNE cruise SO81, and the preliminary results at hand have already improved our knowledge on the geological processes of active continental margins. We are convinced that plausible concepts for the origin of tsunamis and asperities can be developed on the basis of the data collected during SONNE cruises SO81 and SO76. The research of both SONNE cruises are a contribution to the International Decade of Natural Desaster Reduction (IPNDR).
-
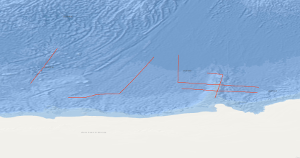
The POLARSTERN cruise ANTVIII/6 from 14. March to 30. April 1990 incorporated an integrated geophysical reconnaissance survey consisting of multichannel seismic measurements in parallel with gravimetric and magnetic measurements. The survey covered the plateaus Maud Rise, Astrid Ridge and Gunnerus Ridge off Queen Maud Land and the oceanic crust in their vicinity. Severe ice and weather conditions allowed seismic work only on the Gunnerus Ridge and on the oceanic crust. Together with previous BGR lines on the Astrid Ridge and the Maud Rise the new data improve considerably the understanding of the area. The main results are: 1. The oldest identified sea-floor spreading anomaly was M11 before the cruise, now it is M24. Thus spreading has begun not only 135 mill. years B.P., but at least 160 mill. years B.P. 2. The Gunnerus Ridge is strongly asymmetric. The mainly weak magnetic anomalies indicate that in contrast to the Astrid Ridge volcanism was not important during its development. 3. The magnetic anomalies are much stronger on the Astrid Ridge and west of it than east of the Astrid Ridge and on the Gunnerus Ridge. 4. The roughness of the basement surface of the oceanic crust varies in a wide range.
-
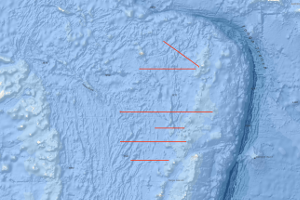
The cruise SO267 ARCHIMEDES I started on December 11th, 2018 in Suva (Fidji) and ended in Suva on January 26th, 2019. Over half of the world´s presently exploited metal deposits were formed during major episodes of crustal growth related to subduction and microplate tectonics. These processes are observed today along the entire margin of the Western Pacific, where complex microplate mosaics offer unique opportunities to study accretion and the emergence of new continental crust. The focus of SO267 was a series of crustal cross-sections at the outer edge of the Indo- Australian Plate, in the largely uncharted waters of the Kingdom of Tonga. The project, entitled “Arc Rifting, Metallogeny and Microplate Evolution – An Integrated Geodynamic, Magmatic and Hydrothermal Study of the Fonualei Rift System”, was designed to document the geological evolution of an emerging microplate mosaic in the NE Lau Basin, a region with some of the fastest growing crust on Earth, and to better understand the sequence of events that cause arc rifting and related magmatic-hydrothermal activity. Using a coordinated approach of high-resolution 2D seismics, electromagnetics and sampling, ARCHIMEDES I imaged the deep structure of the Fonualei Rift system and adjoining back-arc crust of the Niuafo’ou microplate. The goal was to address a major unsolved question concerning crustal growth in complex arc-backarc systems: at what stage in the structural and thermal evolution of the crust does arc rifting occur and seafloor spreading initiate? Planned operations included large-scale reflection and refraction seismic surveys, and a dense program of gravity, magnetics, heat flow, bathymetric mapping and sidescan imaging using the AUV ABYSS and ship-based multibeam systems. This ambitious program was made possible by a close collaboration between GEOMAR and BGR scientists, bringing together diverse expertise and state-of-the-art technologies. To understand the large-scale tectonic processes, we studied 6 different locations within an area of 300 km x 300 km: i) the southern Fonualei Rift Spreading Center (S-FRSC), ii) the region between the S-FRSC and the Eastern Lau Spreading Center (FRSC-ELSC Transfer Zone), iii) the northern tip of the Eastern Lau Spreading Center (ELSC), iv) the northern tip of the Fonualei Rift system (N-FRSC), v) the Mangatolu Triple Junction (MTJ), and vi) the southward propagating Northeast Lau Spreading centre (NELSC). The combined data represent one of the most comprehensive records of microplate formation from the modern oceans.
 www.geodatenkatalog.de (S1F)
www.geodatenkatalog.de (S1F)