Keyword
Bundesrepublik Deutschland
105 record(s)
Provided by
Type of resources
Available actions
Keywords
Update frequencies
Service types
-

-

-
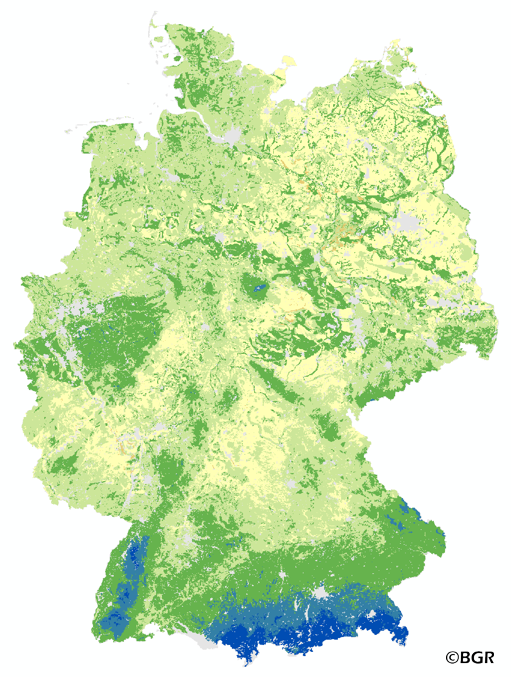
The map of the plant available water in Germany gives an overview of the amount of water which is available for plant growth in the summer period (April – September). It is the sum of the available water holding capacity of soils the precipitation in summer and the amount of capillary rise. The map was made on the basis of the land use stratified soil map of Germany at a scale of 1:1,1000,000, climate data for the period of 1961–1990 and land use information is derived from the Corine Land Cover data set (2006). The method is part of the TUB_BGR approach to model seepage water and is published in the documentation of Ad-hoc-AG Boden (representing the soil experts of the geological services of the German federal states).
-
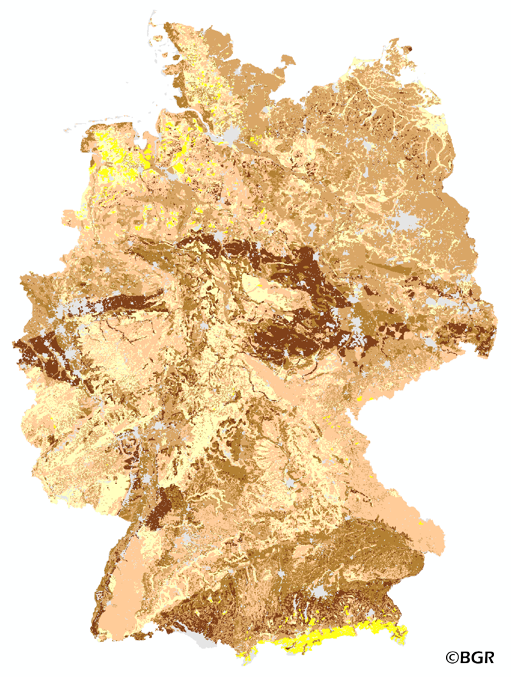

The map of the effective rooting depth gives an overview of the rooting capacity of German soils. The effective rooting depth is the size of the soil reservoir that the plant can reach to get water in years of drought. The effective rooting depth is determined by both crop and soil properties. The rooting depth is derived from profile data of the landuse stratified soil map of Germany at scale 1:1,000,000. The method is taken from Bodenkundliche Kartieranleitung KA4 (1994) and is documented in the Methoden-WIKI of the FISBo BGR. The land use information is derived from the CORINE Land Cover data set (2006).
-

The map of the plant available water in Germany gives an overview of the amount of water which is available for plant growth in the summer period (April – September). It is the sum of the available water holding capacity of soils the precipitation in summer and the amount of capillary rise. The map was made on the basis of the land use stratified soil map of Germany at a scale of 1:1,1000,000, climate data for the period of 1961–1990 and land use information is derived from the Corine Land Cover data set (2006). The method is part of the TUB_BGR approach to model seepage water and is published in the documentation of Ad-hoc-AG Boden (representing the soil experts of the geological services of the German federal states).
-
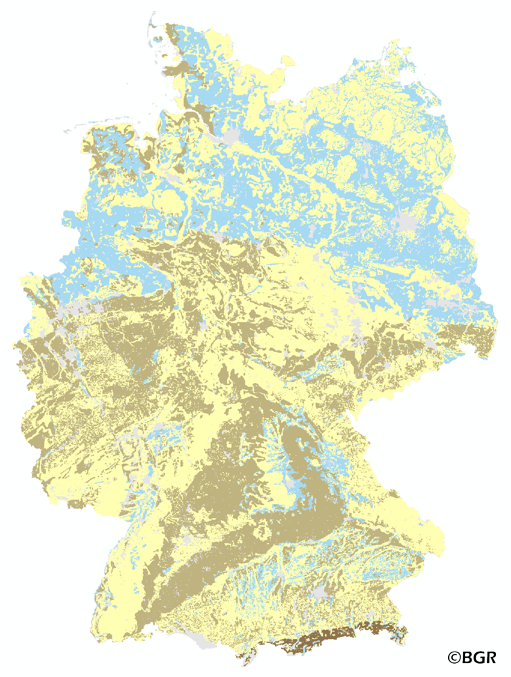
The map of the air capacity of soils in Germany gives an overview of the content of air in a soil at field capacity. The map shows the air, which is available for plant growth from the surface to effective rooting depth, which is derived from land use and soli data. The method is published in the Bodenkundliche Kartieranleitung 4 (1994) and in the documentation of Ad-hoc-AG Boden (representing the soil experts of the geological services of the German federal states). The land use information is derived from the Corine Land Cover data set (2006).
-
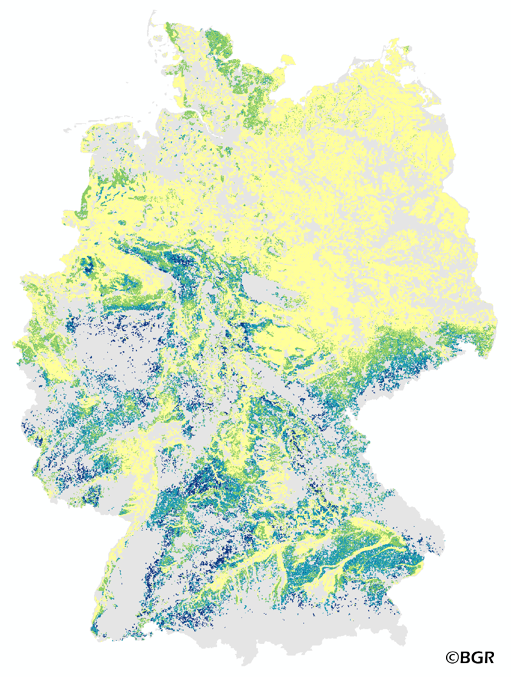
The map of the direct runoff on agricultural soils gives an overview of the average annual amount of precipitation, which does not infiltrate into the soils. It is based on pedological, relief and climatic factors. The map was created by using the empirical SCS – runoff curve number approach. The method was adapted by the Federal Institute for Geosciences and Natural Resources (BGR) as part of the attempt to model the seepage volume in the TUB_BGR method. The land use stratified soil map of Germany at scale 1:1,000,000 was used as pedological input to the model. The relief data was derived from the DEM50 of the BKG. The mean annual precipitation data of the period 1961 -1990 (DWD) is used as an input as well. The land use information is derived from CORINE Land Cover data set (2006).
-

The map of the direct runoff on agricultural soils gives an overview of the average annual amount of precipitation, which does not infiltrate into the soils. It is based on pedological, relief and climatic factors. The map was created by using the empirical SCS – runoff curve number approach. The method was adapted by the Federal Institute for Geosciences and Natural Resources (BGR) as part of the attempt to model the seepage volume in the TUB_BGR method. The land use stratified soil map of Germany at scale 1:1,000,000 was used as pedological input to the model. The relief data was derived from the DEM50 of the BKG. The mean annual precipitation data of the period 1961 -1990 (DWD) is used as an input as well. The land use information is derived from CORINE Land Cover data set (2006).
-

The map of the air capacity of soils in Germany gives an overview of the content of air in a soil at field capacity. The map shows the air, which is available for plant growth from the surface to effective rooting depth, which is derived from land use and soli data. The method is published in the Bodenkundliche Kartieranleitung 4 (1994) and in the documentation of Ad-hoc-AG Boden (representing the soil experts of the geological services of the German federal states). The land use information is derived from the Corine Land Cover data set (2006).
-

The map of the effective rooting depth gives an overview of the rooting capacity of German soils. The effective rooting depth is the size of the soil reservoir that the plant can reach to get water in years of drought. The effective rooting depth is determined by both crop and soil properties. The rooting depth is derived from profile data of the landuse stratified soil map of Germany at scale 1:1,000,000. The method is taken from Bodenkundliche Kartieranleitung KA4 (1994) and is documented in the Methoden-WIKI of the FISBo BGR. The land use information is derived from the CORINE Land Cover data set (2006).
 www.geodatenkatalog.de (S1F)
www.geodatenkatalog.de (S1F)