Keyword
EGDI
21 record(s)
Provided by
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Update frequencies
Service types
-

Since 1999, the Geologic Survey of Baden-Württemberg publishes a statewide geological map series 1 : 50 000 "Karte der mineralischen Rohstoffe 1 : 50 000 (KMR 50)". On it, the distribution of near-surface mineral raw material prospects and occurrences (mainly) and deposits (subordinate) is shown. This continuously completed and updated map currently covers around 60% of the federal state. It is the base for the regional associations in the task of mineral planning. The prospects and occurrences are classified according to different raw material groups (e.g. raw material for crushed stone (limestone, igneous rocks, metamorphic rocks, sand and gravel), raw materials for cement, dimension stone, high purity limestone, gypsum ...). Their spatial delineation is based on various group-specific criteria such as minimum workable thickness, minimum resources, ratio overburden/workable thickness, and so on. It is assumed that they contain deposits as a whole or in parts. In the vast majority of cases, the data is not sufficient for the immediate planning of mining projects, but it does facilitate the selection of exploration areas. The name of each area (e.g. L 6926-3) consists of three parts. L = roman rnumeral fo 50, 6926 = sheet number of the topographic map 1 : 50 000, 3 = number of the area/mineral occurrence shown on this sheet. Co-occurring land-use conflicts, e.g. water protection areas and nature conservation areas, forestry and agriculture, are not taken into account in the processing of KMR 50. Their assessment is the task of land use planning, the licensing authorities and the companies interested in mining. The data is stored in the statewide raw material area database "olan-db" of the LGRB.
-

Since the end of the 1980ies the geological, areal and production data of operating mining sites have been collected systematically by LGRB. The periodic update of this information is carried out every four or five years. Main reasons are 1) the preparation of the periodic follow-up of the 12 regional development plans, 2) the work on the near-surface mineral raw material maps published by LGRB, and 3) the periodical editing of the state report for near-surface mineral raw materials published by LGRB at the start of each new election period. The geological data include a detailed documentation of the thickness, petrography and quality of mined rock(s) and the overburden as well as geochemical data gained from rock samples. The areal data refer both to the permitted mining area (zones of recultivation, work and expansion) and to possible areas for the mine expansion (the latter are confidential). Due to the quick spatiotemporal variability of these data, here all mining sites are shown as point data. The confidential annual production data are the basis for the periodic raw material report. In addition, another data are collected, e.g. for the mining permission, the delivery area and the subsequent land use. All these data are stored in the mining site database of the LGRB (Rohstoffgewinnungs-stellendatenbank = RGDB). This one comprises also the data for abandoned mining sites and mines. In total, actual (2021) about 14.000 data records are stored. The name of each mining site (e.g. RG 6826-3) consists of three parts. RG is the abbreviation for "Rohstoffgewinnungsstelle". the following four-digit number means the number of the relevant topographic map 1 : 25.000. The last number means the serial number of the mining site; serial numbers 1-99 mark operating mining sites gathered since the end of the 1980ies ( (today partially already closed) , such > 100 mark abandoned mining sites collected before 1980 and such > 300 mark data of mining sites and mines collected in the course of actual raw material mapping. The mintell4eu data set comprises all mining sites with serial numbers 1-99. In addition, the most important abandoned mines of former or probably still ongoing economic importance.
-
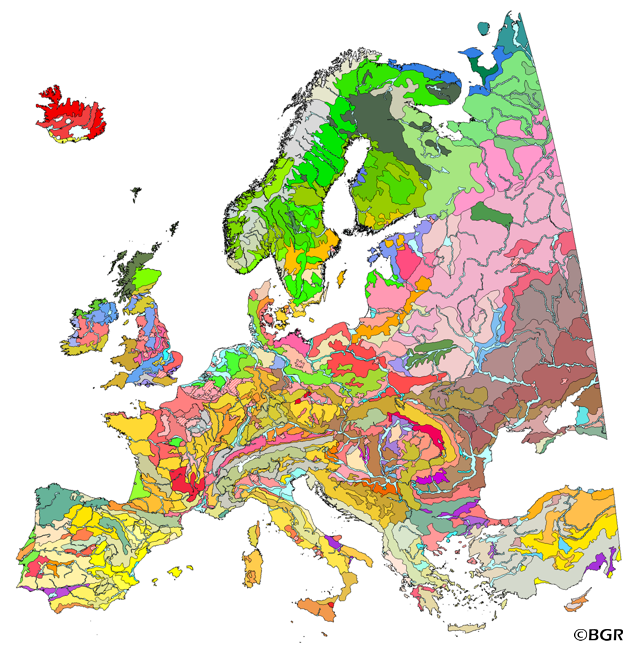
The map of the "Soil Regions of the European Union and Adjacent Countries 1:5,000,000 (Version 2.0)" is published by the Federal Institute of Geosciences and Natural Resources (BGR), in partnership with the Joint Research Center (JRC, Ispra). The soil regions map is intended to support the current national mapping activities towards a European 1:250,000 datbase by stratifying similar regional soil associations into a hierarchical concept. Only by stratification, the complexity of soils can be systematically structured so that the complex 1:250,000 legend can be handled in cross-national and contintental-level applications. Soil regions are natural, cross-regional soil geographical units which perform the highest spatial and content-based aggregation of European soils. They represent the frame conditions for soil development at the landscape level. The soil regions are presented at scale 1:5,000,000. Thus, its borders are highly generalized. Because of its low resolution, the map units absorb atypical soils and associations of soils, which are only described in higher resolution soil maps. The delineation of the soil regions is expected to be refined (and probably improved by its content) during the actual 1:250,000 mapping process. Thus, updating can be expected in the future. Currently, the soil regions map is the only graphical soil representation in Europe which has been developed using fully comparable and harmonized basic data at the continental level (climate, hydrography, relief, geology, vegetation): the interpretation of this input data, and the utilization of expert knowledge (including the interpretation of regional soil maps) has been done using one common methodology, developed and applied consistently throughout the whole mapping area by an experienced international soil mapper (Dr. Reinhard Hartwich, former member of BGR, and co-author of the 1998 Manual of Procedures). The methodology is extensively described in the Explanatory Notes (German), and in the revised Manual of Procedures which is expected to be completed soon. It is highly recommended to apply and interpret the map using the map comments and descriptions as provided in the explanatory notes (German: Hartwich et al. 2005; English: revision of the Manual of Procedures, initial version: Finke et al. 2001).
-

Compilation of the European Quaternary marine geology (section of Germany). The original map consists of data at highest available spatial resolution, map scale („multi-resolution“-concept) and data completeness vary depending on the project partner (as of 2019 April). Project partners are the national geological services of the participating countries. According to the Data Specification on Geology (D2.8.II.4_v3.0) the geological map (section of Germany) provides INSPIRE-compliant data. The WMS EMODnet-DE Quaternary (INSPIRE) contains layers of the geologic units (GE.GeologicUnit) displayed correspondingly to the INSPIRE portrayal rules. The geologic units are represented graphically by stratigraphy (GE.GeologicUnit.AgeOfRocks) and lithology (GE.GeologicUnit.Lithology). The portrayal of the lithology is defined by the first named rock. Via the getFeatureInfo request the user obtains detailed information on the lithology, stratigraphy (age) and genesis (event environment and event process).
-
.png)
The WMS GK1000 (INSPIRE) represents the surface geology of Germany and adjacent areas on a scale of 1:1,000,000. According to the Data Specification on Geology (D2.8.II.4_v3.0) the geological map provides INSPIRE-compliant data. The WMS GK1000 (INSPIRE) contains layers of the geologic units (GE.GeologicUnit), faults (GE.GeologicFault) and marginal position of the ice shield (GE. NaturalGeomorphologicFeature) displayed correspondingly to the INSPIRE portrayal rules. The geologic units are represented graphically by stratigraphy (GE.GeologicUnit.AgeOfRocks) and lithology (GE.GeologicUnit.Lithology). For different geochronologic minimum and maximum ages, e.g. Carboniferous - Permian, the portrayal is defined by the color of the geochronologic minimum age (olderNamedAge). The portrayal of the lithology is defined by the rock or rock group representing the main part of the lithological composition of the geologic unit. In case of the geologic units the user obtains detailed information via the getFeatureInfo request on the lithology, stratigraphy (age) and genesis (event environment and event process).
-
.png)
The GK1000 (INSPIRE) represents the surface geology of Germany and adjacent areas on a scale of 1:1,000,000. According to the Data Specification on Geology (D2.8.II.4_v3.0) the content of the geological map is stored in three INSPIRE-compliant GML files: GK1000_GeologicUnit.gml contains the geologic units, GK1000_GeologicStructure.gml comprises the faults and GK1000_NaturalGeomorphologicFeature.gml represents the marginal position of the ice shield. The GML files together with a Readme.txt file are provided in ZIP format (GK1000-INSPIRE.zip). The Readme.text file (German/English) contains detailed information on the GML files content. Data transformation was proceeded by using the INSPIRE Solution Pack for FME according to the INSPIRE requirements.
-
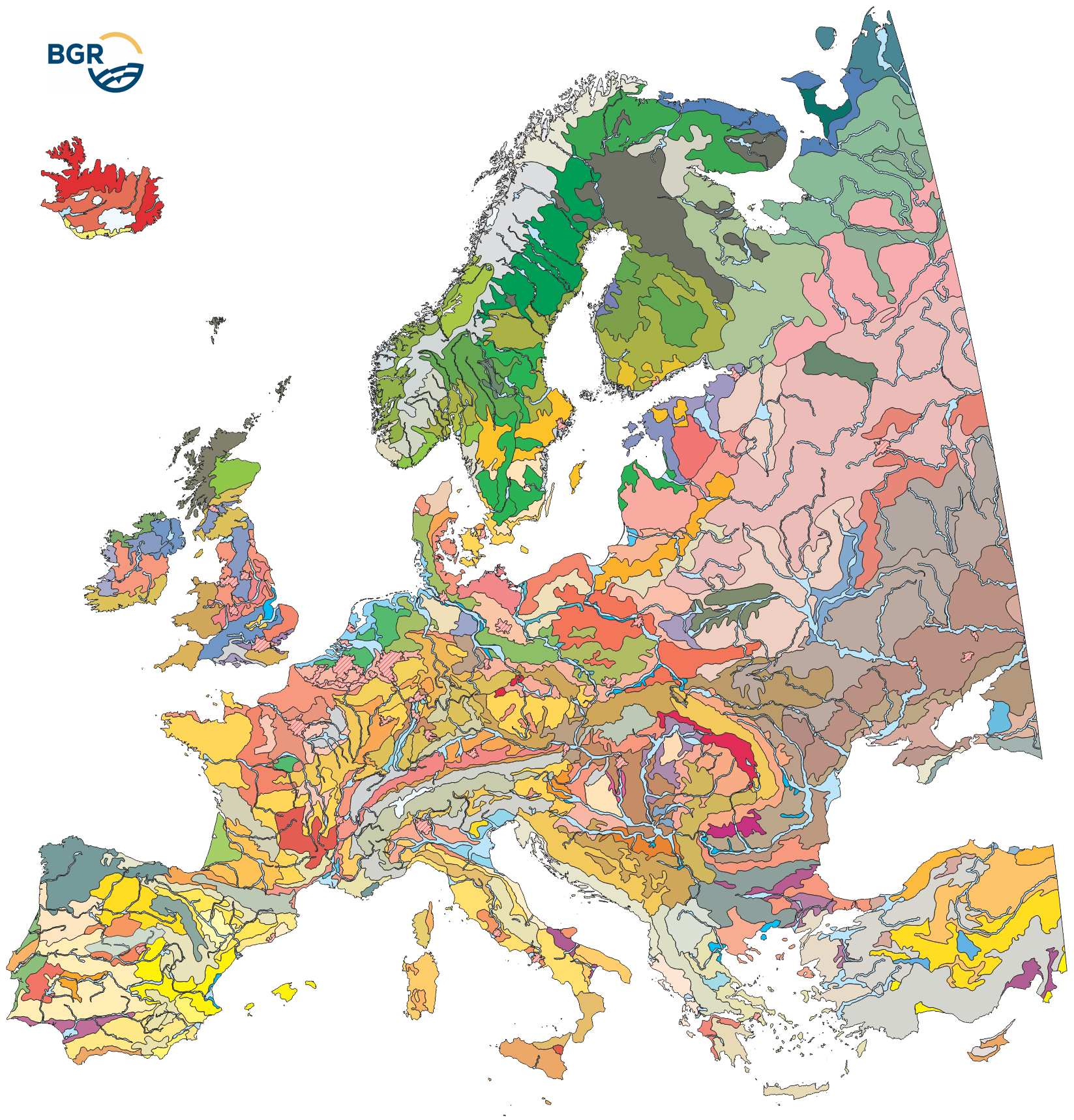
The map of the "Soil Regions of the European Union and Adjacent Countries 1 : 5 000 000 (Version 2.0)" is published by the Federal Institute of Geosciences and Natural Resources (BGR), in partnership with the Joint Research Center (JRC, Ispra). The soil regions map is intended to support the current national mapping activities towards a European 1:250,000 datbase by stratifying similar regional soil associations into a hierarchical concept. Only by stratification, the complexity of soils can be systematically structured so that the complex 1:250.000 legend can be handled in cross-national and contintental-level applications. Soil regions are natural, cross-regional soil geographical units which perform the highest spatial and content-based aggregation of European soils. They represent the frame conditions for soil development at the landscape level. The soil regions are presented at scale 1:5,000,000. Thus, its borders are highly generalized. Because of its low resolution, the map units absorb atypical soils and associations of soils, which are only described in higher resolution soil maps. The delineation of the soil regions is expected to be refined (and probably improved by its content) during the actual 1:250,000 mapping process. Thus, updating can be expected in the future. Currently, the soil regions map is the only graphical soil representation in Europe which has been developed using fully comparable and harmonized basic data at the continental level (climate, hydrography, relief, geology, vegetation): the interpretation of this input data, and the utilization of expert knowledge (including the interpretation of regional soil maps) has been done using one common methodology, developed and applied consistently throughout the whole mapping area by an experienced international soil mapper (Dr. Reinhard Hartwich, former member of BGR, and co-author of the 1998 Manual of Procedures). The methodology is extensively described in the Explanatory Notes (German), and in the revised Manual of Procedures which is expected to be completed soon.
-
The “Geological Map of Germany 1:1,000,000 OneGeology-Europe (GK1000-1GE)” shows Germany’s surface geology: All geological units are described by their age (stratigraphy) and composition (lithology). The geological units and terms used in this map were semantically harmonized within the OneGeology-Europe project and have been - in a number of regions - geometrically and semantically made consistent with the neighbouring OneGeology-Europe participants.
-

This Downloadservice contains point locations of near-surface mineral raw material occurrences and mining sites in Baden-Württemberg (BW), which is one of 16 states of the Federal Republic of Germany. The information is harmonized according to the specifications of the MIN4EU database model as part of the Mintell4EU project. BW is rich in near-surface mineral raw materials. The most important are 1) Quaternary sands and gravels (Upper Rhine Graben Valley and glacial sediments of Upper Swabia), 2) Paleozoic rocks (mainly metamorphic rocks and granites, minor Permian volcanic rocks) in the Black Forest and the Odenwald, and 3) Middle Triassic (Southwest German scarplands) and Upper Jurassic (Swabian Alb) limestones. The deep-lying raw materials (various gangue ores, barite, fluorite, uranium ores), which were mined mainly in the Black Forest, are currently of no importance, with the exception of the still ongoing extraction of barite and fluorite in the Clara mine. In the future, some deposits could regain importance as raw material prices rise. Almost 100 million tons of mostly near-surface mineral raw materials are extracted annually in BW in currently about 500 mining sites (survey year: 2017). The annual raw material consumption is approx. 9 tons/inhabitant. At the beginning of the 2000s, there were still around 630 mining sites. This decline is due to both concentration processes and depletion of deposits. Since the end of the 1980ies the geological, areal and production data of operating mining sites have been collected systematically by LGRB. They are the basis for the periodic raw material report edited by LGRB and for the calculation of the need of mineral raw materials. Manly these pits, beside some important historic mines, are shown in the layer "MIN4EU LGRB-BW: mining sites - harmonized dataset". Another important task of the LGRB is to advise the regional planning authorities on securing mineral raw material supply. Beside the calculation of the need of mineral raw materials supply for the two planning periods (2 x 15 or 2x 20 years), the knowledge of mineral occurrences of proven or estimated economic value is important. After some preliminary stages, the LGRB is producing the Map of Mineral Resources in Baden-Württemberg 1 : 50,000 (KMR 50) as a basis and planning map for this purpose. On it, the distribution of near-surface mineral raw material prospects and occurrences (mainly) and deposits (subordinate) is shown. This continuously completed and updated map currently covers actually around 60% of the federal state. These occurrences are the topic of the second layer theme "MIN4EU LGRB-BW: near-surface mineral raw material occurrences - harmonized dataset".
-

The “Geological Map of Germany 1:1,000,000 OneGeology-Europe (GK1000-1GE)” shows Germany’s surface geology: All geological units are described by their age (stratigraphy) and composition (lithology). The geological units and terms used in this map were semantically harmonized within the OneGeology-Europe project and have been - in a number of regions - geometrically and semantically made consistent with the neighbouring OneGeology-Europe participants.
 www.geodatenkatalog.de (S3L)
www.geodatenkatalog.de (S3L)