Keyword
Sentinel-1
20 record(s)
Provided by
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Update frequencies
Service types
-
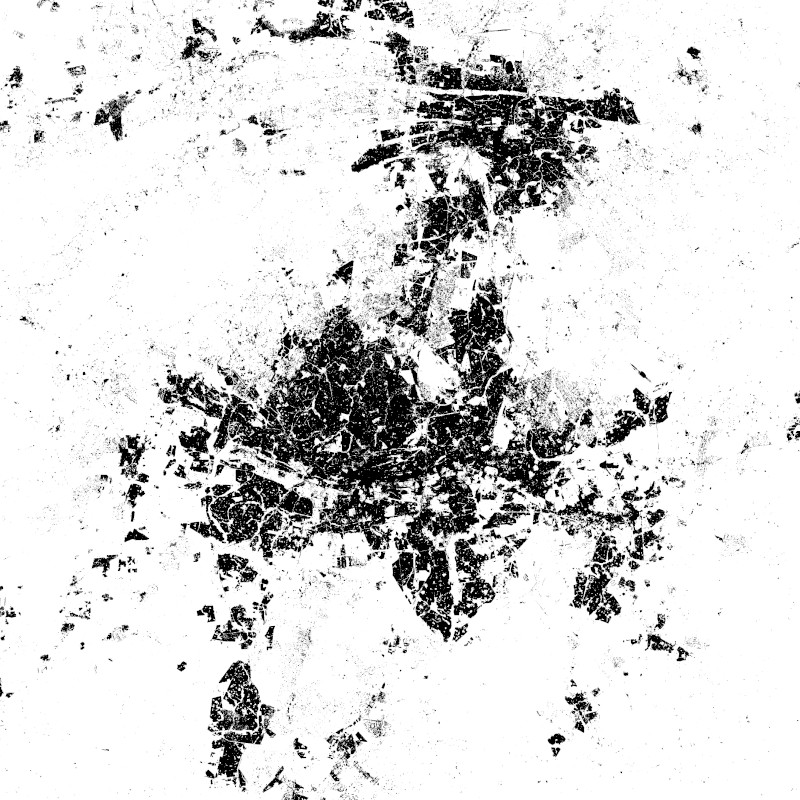

The World Settlement Footprint WSF 2015 version 2 (WSF2015 v2) is a 10m resolution binary mask outlining the extent of human settlements globally for the year 2015. Specifically, the WSF2015 v2 is a pilot product generated by combining multiple datasets, namely: • The WSF2015 v1 derived at 10m spatial resolution by means of 2014-2015 multitemporal Landsat-8 and Sentinel-1 imagery (of which ~217K and ~107K scenes have been processed, respectively); https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-020-00580-5 • The High Resolution Settlement Layer (HRSL) generated by the Connectivity Lab team at Facebook through the employment of 2016 DigitalGlobe VHR satellite imagery and publicly released at 30m spatial resolution for 214 countries; https://arxiv.org/pdf/1712.05839.pdf • The novel WSF2019 v1 derived at 10m spatial resolution by means of 2019 multitemporal Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 imagery (of which ~ 1.2M and ~1.8M scenes have been processed, respectively); https://doi.org/10.1553/giscience2021_01_s33 The WSF2015 v1 demonstrated to be highly accurate, outperforming all similar existing global layers; however, the use of Landsat imagery prevented a proper detection of very small structures, mostly due to their reduced scale. Based on an extensive qualitative assessment, wherever available the HRSL layer shows instead a systematic underestimation of larger settlements, whereas it proves particularly effective in identifying smaller clusters of buildings down to single houses, thanks to the employment of 2016 VHR imagery. The WSF2015v v2 has been then generated by: i) merging the WSF2015 v1 and HRSL (after resampling to 10m resolution and disregarding the population density information attached); and ii) masking the outcome by means of the WSF2019 product, which exhibits even higher detail and accuracy, also thanks to the use of Sentinel-2 data and the proper employment of state-of-the-art ancillary datasets (which allowed, for instance, to effectively mask out all roads globally from motorways to residential).
-
The World Settlement Footprint (WSF) 2019 is a 10m resolution binary mask outlining the extent of human settlements globally derived by means of 2019 multitemporal Sentinel-1 (S1) and Sentinel-2 (S2) imagery. Based on the hypothesis that settlements generally show a more stable behavior with respect to most land-cover classes, temporal statistics are calculated for both S1- and S2-based indices. In particular, a comprehensive analysis has been performed by exploiting a number of reference building outlines to identify the most suitable set of temporal features (ultimately including 6 from S1 and 25 from S2). Training points for the settlement and non-settlement class are then generated by thresholding specific features, which varies depending on the 30 climate types of the well-established Köppen Geiger scheme. Next, binary classification based on Random Forest is applied and, finally, a dedicated post-processing is performed where ancillary datasets are employed to further reduce omission and commission errors. Here, the whole classification process has been entirely carried out within the Google Earth Engine platform. To assess the high accuracy and reliability of the WSF2019, two independent crowd-sourcing-based validation exercises have been carried out with the support of Google and Mapswipe, respectively, where overall 1M reference labels have been collected based photointerpretation of very high-resolution optical imagery.
-

The World Settlement Footprint (WSF) 3D provides detailed quantification of the average height, total volume, total area and the fraction of buildings at 90 m resolution at a global scale. It is generated using a modified version of the World Settlement Footprint human settlements mask derived from Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 satellite imagery in combination with digital elevation data and radar imagery collected by the TanDEM-X mission. The framework includes three basic workflows: i) the estimation of the mean building height based on an analysis of height differences along potential building edges, ii) the determination of building fraction and total building area within each 90 m cell, and iii) the combination of the height information and building area in order to determine the average height and total built-up volume at 90 m gridding. In addition, global height information on skyscrapers and high-rise buildings provided by the Emporis database is integrated into the processing framework, to improve the WSF 3D Building Height and subsequently the Building Volume Layer. A comprehensive validation campaign has been performed to assess the accuracy of the dataset quantitatively by using VHR 3D building models from 19 globally distributed regions (~86,000 km2) as reference data. The WSF 3D standard layers are provided in the format of Lempel-Ziv-Welch (LZW)-compressed GeoTiff files, with each file - or image tile - covering an area of 1 x 1 ° geographical lat/lon at a geometric resolution of 2.8 arcsec (~ 90 m at the equator). Following the system established by the TDX-DEM mission, the latitude resolution is decreased in multiple steps when moving towards the poles to compensate for the reduced circumference of the Earth.
-

SWIM Water Extent is a global surface water product at 10 m pixel spacing based on Sentinel-1/2 data. The collection contains binary layers indicating open surface water for each Sentinel-1/2 scene. Clouds and cloud shadows are removed using ukis-csmask (see: https://github.com/dlr-eoc/ukis-csmask ) and are represented as NoData. The water extent extraction is based on convolutional neural networks (CNN). For further information, please see the following publications: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2019.05.022 and https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11192330
-

The Tree Species Germany product provides a map of dominant tree species across Germany for the year 2022 at a spatial resolution of 10 meters. The map depicts the distribution of ten tree species groups derived from multi-temporal optical Sentinel-2 data, radar data from Sentinel-1, and a digital elevation model. The input features explicitly incorporate phenological information to capture seasonal vegetation dynamics relevant for species discrimination. A total of over 80,000 training and test samples were compiled from publicly accessible sources, including urban tree inventories, Google Earth Pro, Google Street View, and field observations. The final classification was generated using an XGBoost machine learning algorithm. The Tree Species Germany product achieves an overall F1-score of 0.89. For the dominant species pine, spruce, beech, and oak, class-wise F1-scores range from 0.76 to 0.98, while F1-scores for other widespread species such as birch, alder, larch, Douglas fir, and fir range from 0.88 to 0.96. The product provides a consistent, high-resolution, and up-to-date representation of tree species distribution across Germany. Its transferable, cost-efficient, and repeatable methodology enables reliable large-scale forest monitoring and offers a valuable basis for assessing spatial patterns and temporal changes in forest composition in the context of ongoing climatic and environmental dynamics.
-

The PolarLakes dataset provides bi-weekly observations of supraglacial lakes on Antarctic ice shelves, utilizing imagery from Sentinel-2 and Sentinel-1 to address time series gaps caused by frequent cloud cover. These observations detect the extents of supraglacial lakes with a U-Net model for every two weeks from November to March, with each sensor operating independently before the data is merged. The resulting bi-weekly product reflects the maximum lake extents for the first and second halves of each month. When combined for an entire season, the dataset consolidates all bi-weekly records over these five months, allowing for analysis of the maximum lake extent per season and the frequency of lake formation, which can occur up to ten times (5 months á two weeks). The year indicated in the dataset corresponds to January of the melt season, as this month typically experiences the highest melt rates (e.g., 2023 refers to the season from November 2022 to March 2023). The aggregation of all annual datasets creates a recurrence layer that illustrates the frequency of lake presence throughout the entire observation period, which spans from 2014 to 2024, depending on satellite data availability for each ice shelf. The PolarLakes dataset provides valuable insights into the dynamics of supraglacial lakes and serves as a crucial resource for hydrological and climate modeling.
-

The SAR4Tectonics project aims to provide open-access, global measurements of ground deformation in high-strain areas near tectonic plate boundaries. By leveraging the capabilities of the Persistent and Distributed Scatterer (PS/DS) technique with Sentinel-1 SAR images, the project seeks to deliver comprehensive and accurate data on ground deformation, which is crucial for understanding geological processes, assessing seismic risks in these regions, and advance our understanding of Earth's dynamic processes in general. The PS/DS technique offers significantly denser spatial coverage than GNSS, enabling the detection of more localized deformation signals. For the first time, such a vast and detailed dataset is made publicly available. By making this data openly accessible, the SAR4Tectonics project hopes to reduce the burden of SAR data processing for geoscientists, facilitating future studies.The project involved processing 6.5 years of SAR data, focusing on areas where the second invariant of strain exceeds 3 nanostrain per year. Various error corrections were employed, including tropospheric delay correction using ECMWF reanalysis data, ionospheric mitigation via CODE total electron content maps, and solid earth tide modeling. Additionally, the impact of vegetation and soil moisture on distributed scatterers was minimized through a full covariance matrix (phase linking) approach, and the results were calibrated using GNSS data. The final dataset includes line-of-sight average velocity maps, deformation time series, projection vectors, and reference plate modeled velocities.
-

The dataset is based on an analysis combining Sentinel-1 (SAR), -2 (Multispectral) and GEDI (Global Ecosystem Dynamics Investigation, LiDAR) data to model vegetation structure information. The derived products show high-spatial resolution maps (10 m) of total canopy cover (cover density in %), Foliage height diversity (Fhd) index in meter, Plant area index (Pai) in meter and canopy height (rh95) in meter.
-
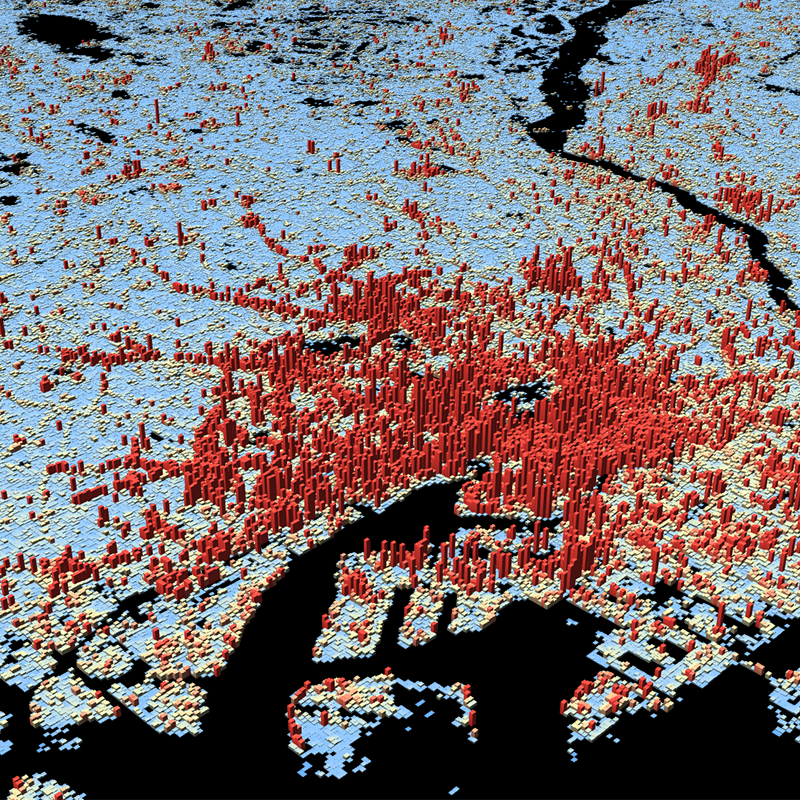
This dataset is a derivative of the WSF3D raster dataset tailored for the web. As a tiled vector dataset, it enables dynamic client-side visualization of the WSF3D metrics
-
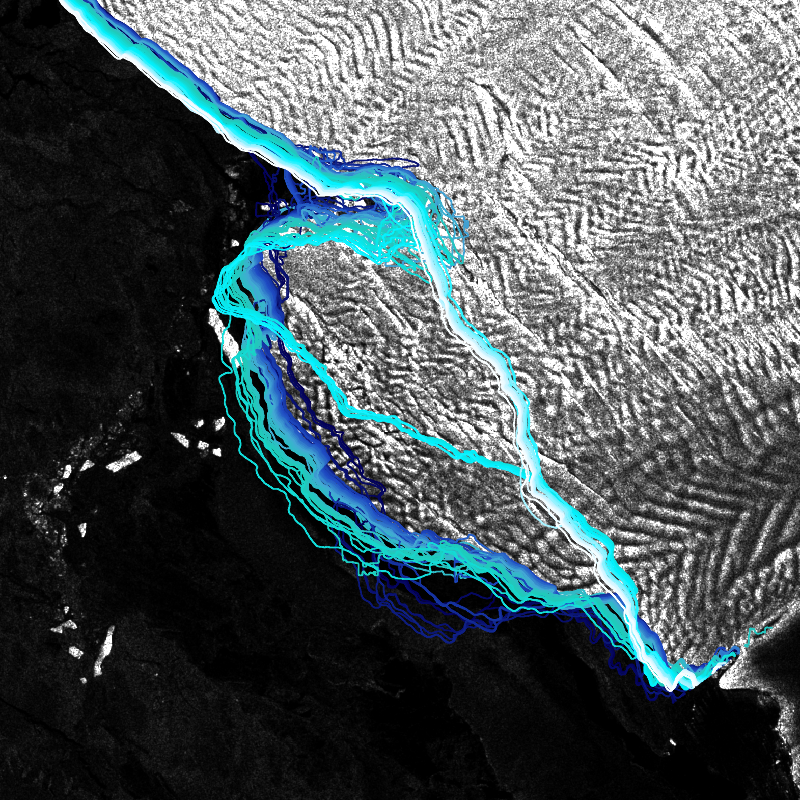
IceLines (Ice Shelf and Glacier Front Time Series) is an automated calving front monitoring service providing monthly ice shelf front time series of major Antarctic ice shelves. The provided time series allows to discover the dynamics of ice shelf front changes and calving events. The front positions are automatically derived from Sentinel-1 data based on a deep neuronal network called HED-U-Net. The time series covers the timespan 2014 to today (partly limited due to Sentinel-1 data availability). Incorrectly extracted fronts are truncated which might lead to gaps in the time series especially between December to March due to strong surface melt. Annual averages are calculated based on the extracted monthly fronts (excluding the summer months) and provide more robust results due to temporal aggregation
 www.geodatenkatalog.de (S3L)
www.geodatenkatalog.de (S3L)