Keyword
EOC
142 record(s)
Provided by
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Update frequencies
Service types
-

The map shows the elevation of the surroundings of the Al Zaatari refugee camp in Jordan. The elevation information is derived from ASTER GDEM 2 data (vertical accuracy +/- 6m). Furthermore basic reference information, digitized on the basis of WorldView-2 satellite data acquired on January 03, 2013, at 08:52:52 UTC and LANDSAT-7 data acquired on December 16, 2012 at 08:07:11 UTC, is depicted. Not all settlements are captured. The results have not been validated in the field. ASTER GDEM 2 data as well as a hillshade derived from this data is used as backdrop. Please note, that information on elevation derived from ASTER data does not apply for the refugee camp area. ASTER data was acquired before 2011 and the elevation might have changed due to construction works. The products elaborated for this Rapid Mapping Activity are realised to the best of our ability, within a very short time frame, optimising the material available. All geographic information has limitations due to the scale, resolution, date and interpretation of the original source materials. No liability concerning the content or the use thereof is assumed by the producer. The ZKI crisis maps are constantly updated. Please make sure to visit http://www.zki.dlr.de for the latest version of this product.
-
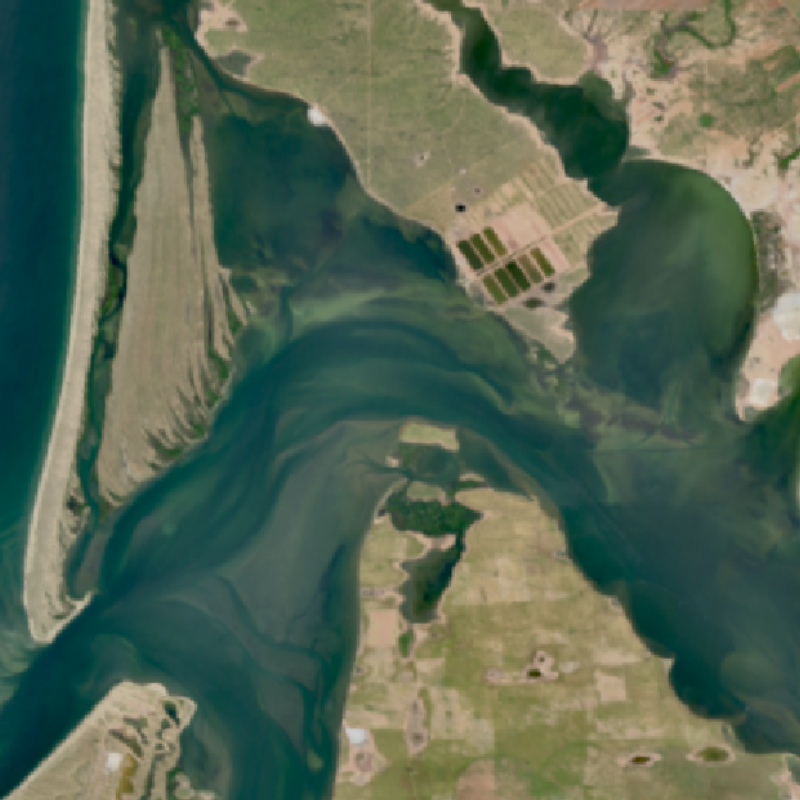

The EnMAP HSI L2A dataset collection comprises a standardized, consistent, systematically processed, and cloud-native level-2A dataset series for the entire mission. It is especially useful for big data or time series analyses. The dataset is processed with the atmospheric correction over land processor and is provided in cloud-optimized GeoTIFF format for direct access and download. The metadata follows the CEOS Analysis Ready Data (CEOS-ARD) framework. The database is constantly updated with newly acquired data. The Environmental Mapping and Analysis Program (EnMAP) is a German hyperspectral satellite mission that monitors and characterizes Earth’s environment on a global scale. EnMAP delivers accurate data that provides information on the status and evolution of terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems, supporting environmental monitoring, management, and decision-making. For more information, please see the mission website: https://www.enmap.org/mission/
-

The map shows the Al Zaatari refugee camp in Jordan. It is situated approx. 12 km from the Syrian border and in close proximity to the city of Al Mafraq (10 km). The camp was set up on July 28, 2012, to shelter refugees fleeing the conflict in Syria. The map shows general characteristics of the camp infrastructure, including camp extent, location of shelters, containers and facility buildings, road infrastructure and the runway area. For a more detailed view parts of the camp area are also shown in the zoom boxes. The vector data have been digitized on the basis of WorldView-2 satellite data (0.5 m spatial resolution) acquired on January 03, 2013. The results have not been validated in the field. WorldView-2 satellite data acquired on January 03, 2013, is used as backdrop. The products elaborated for this Rapid Mapping Activity are realised to the best of our ability, within a very short time frame, optimising the material available. All geographic information has limitations due to the scale, resolution, date and interpretation of the original source materials. No liability concerning the content or the use thereof is assumed by the producer. The ZKI crisis maps are constantly updated.
-

The Al Zaatari refugee camp in Jordan is situated approx. 12 km from the Syrian border and in close proximity to the city of Al Mafraq (10 km). Due to heavy rainfall in the region parts of the Zaatari camp are affected by flooding. The map shows the flood situation derived by semi-automatic image analysis of TerraSAR-X data acquired on January 10, 2013 at 03:38:49 UTC. Furthermore basic reference information, digitized on the basis of WorldView-2 satellite data acquired on January 03, 2013, at 08:52:52 UTC, is depicted. The contour lines were derived from ASTER GDEM 2 data (vertical accuracy +/- 6m). For a more detailed view on the flood situation, parts of the camp area are also shown in the zoom boxes. The results of the image interpretation and analysis have not been validated in the field. WorldView-2 satellite data acquired on January 03, 2013, is used as backdrop. Please note that flood waters in settlement areas might not be fully captured and the water extent might be underestimated due to sensor characteristics. Thus especially shallow water bodies might not be fully captured. The products elaborated for this Rapid Mapping Activity are realised to the best of our ability, within a very short time frame, optimising the material available. All geographic information has limitations due to the scale, resolution, date and interpretation of the original source materials. No liability concerning the content or the use thereof is assumed by the producer. The ZKI crisis maps are constantly updated. Please make sure to visit http://www.zki.dlr.de for the latest version of this product.
-

The map shows the Al Zaatari refugee camp in Jordan. It is situated approx. 12 km from the Syrian border and in close proximity to the city of Al Mafraq (10 km). The camp was set up on July 28, 2012 to shelter refugees fleeing the conflict in Syria. The vector data have been digitized on the basis of WorldView-2 satellite data (0.5m spatial resolution) acquired on January 03, 2013. The results have not been validated in the field. WorldView-2 satellite data acquired on January 03, 2013 is used as backdrop. The products elaborated for this Rapid Mapping Activity are realised to the best of our ability, within a very short time frame, optimising the material available. All geographic information has limitations due to the scale, resolution, date and interpretation of the original source materials. No liability concerning the content or the use thereof is assumed by the producer. The ZKI crisis maps are constantly updated. Please make sure to visit http://www.zki.dlr.de for the latest version of this product.
-
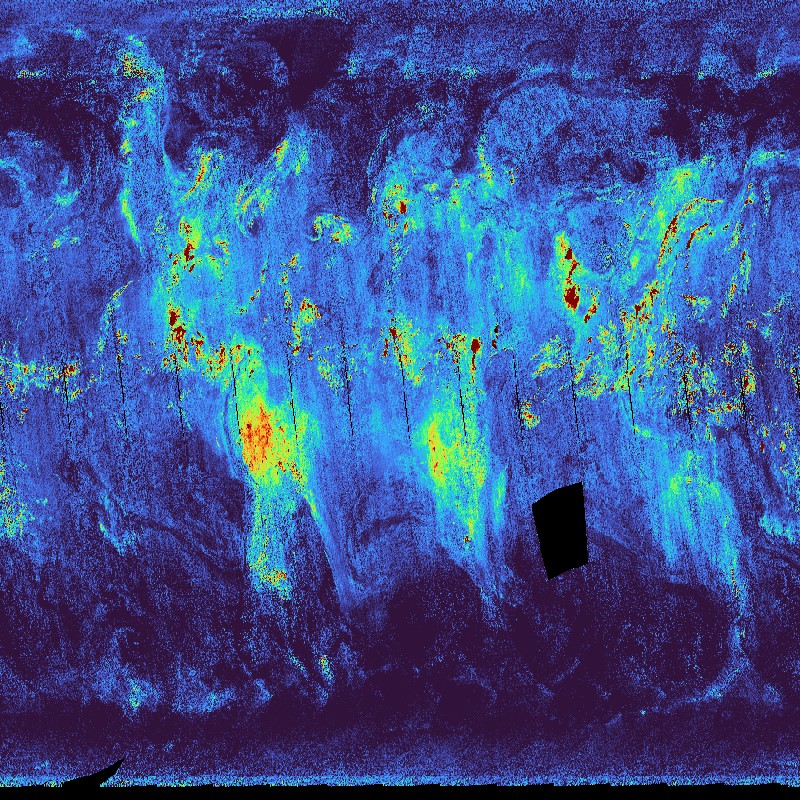
Formaldehyde (HCHO) concentration (globally) as derived from Sentinel-5P/TROPOMI observations. Major HCHO sources are vegetation, fires, traffic and industrial sources. Daily observations are binned onto a regular latitude-longitude grid. The TROPOMI instrument aboard the SENTINEL-5P space craft is a nadir-viewing, imaging spectrometer covering wavelength bands between the ultraviolet and the shortwave infra-red. TROPOMI's purpose is to measure atmospheric properties and constituents. It is contributing to monitoring air quality and providing critical information to services and decision makers. The instrument uses passive remote sensing techniques by measuring the Top Of Atmosphere (TOA) solar radiation reflected by and radiated from the earth and its atmosphere. The four spectrometers of TROPOMI cover the ultraviolet (UV), visible (VIS), Near Infra-Red (NIR) and Short Wavelength Infra-Red (SWIR) domains of the electromagnetic spectrum, allowing operational retrieval of the following trace gas constituents: Ozone (O3), Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2), Sulfur Dioxide (SO2), Formaldehyde (HCHO), Carbon Monoxide (CO) and Methane (CH4). Within the INPULS project, innovative algorithms and processors for the generation of Level 3 and Level 4 products, improved data discovery and access technologies as well as server-side analytics for the users are developed.
-

This dataset provides monthly maximum Land Surface Temperature (LST) values over Europe, derived from 1-km AVHRR observations. The data is generated by DLR and provided in the framework of the TIMELINE project. LST values are retrieved using physically-based split- and mono-window algorithms and corrected for atmospheric influences and surface emissivity. Only cloud-free observations with sensor view angles below 50 degrees are used. Due to reliance on infrared observations, data may be limited under persistent cloud cover. To ensure temporal consistency across sensors and overpass times, an orbit drift correction method was applied. This method harmonizes LST values to a fixed reference time of 13:00 local solar time, approximating the daily maximum temperature. The dataset is gridded in a 1-km LAEA ETRS89 projection. The product is provided in four tiles, covering the extent of the European Environmental Agency (EEA) reference grid, which includes the area from 900 000 m East and 900 000m North to 7 400 000m East and 5 500 000m North. The TIMELINE (TIMe Series Processing of Medium Resolution Earth Observation Data assessing Long-Term Dynamics In our Natural Environment) project, led by the German Remote Sensing Data Center (DFD) of the German Aerospace Center (DLR), focuses on generating a consistent, multi-decadal time series derived from NOAA and Metop AVHRR data. Spanning more than 40 years from the early 1980s to the present this dataset covers Europe and North Africa. TIMELINE establishes an operational environment for the systematic reprocessing of AVHRR raw data into Level 1b, Level 2, and Level 3 geoinformation products at 1.1 km spatial resolution. These products maintain uniform standards in format, projection, and spatial coverage. The dataset includes a comprehensive suite of land and atmospheric parameters such as atmospherically corrected surface reflectance, NDVI, snow cover, fire hotspots, burnt area, land and sea surface temperatures, and various cloud physical properties (e.g., cloud top temperature). By combining traditional and innovative remote sensing products with robust processing algorithms and state-of-the-art validation techniques, TIMELINE provides a unique, high-quality dataset for global change research.
-
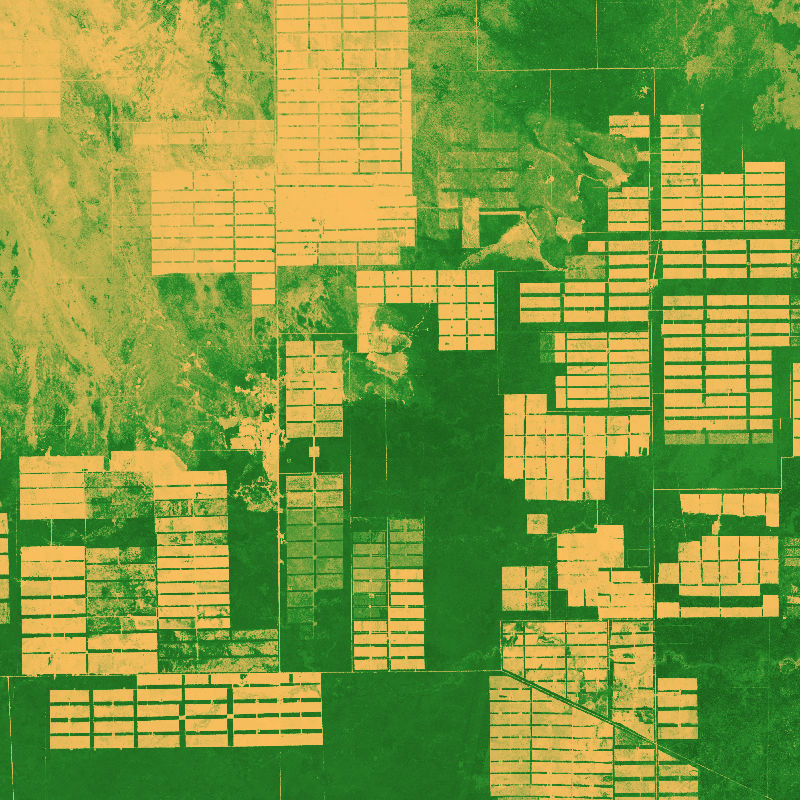

The dataset is based on an analysis combining Sentinel-1 (SAR), -2 (Multispectral) and GEDI (Global Ecosystem Dynamics Investigation, LiDAR) data to model vegetation structure information. The derived products show high-spatial resolution maps (10 m) of total canopy cover (cover density in %), Foliage height diversity (Fhd) index in meter, Plant area index (Pai) in meter and canopy height (rh95) in meter.
-
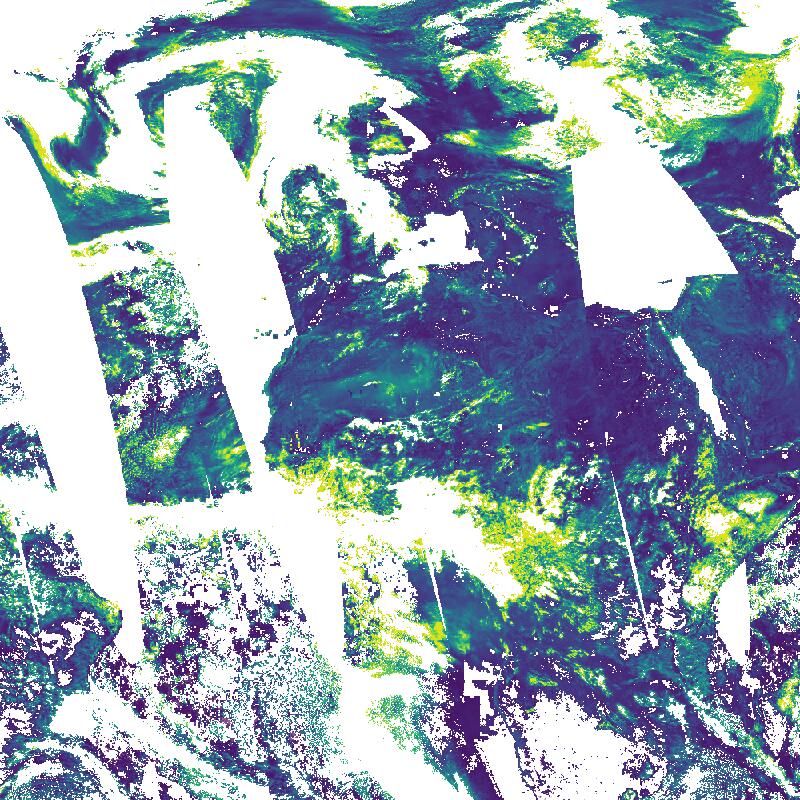

Aerosol optical depth (AOD) as derived from TROPOMI observations. AOD describes the attenuation of the transmitted radiant power by the absence of aerosols. Attenuation can be caused by absorption and/or scattering. AOD is the primary parameter to evaluate the impact of aerosols on weather and climate. Daily AOD observations are binned onto a regular latitude-longitude grid. The TROPOMI instrument onboard the Copernicus SENTINEL-5 Precursor satellite is a nadir-viewing, imaging spectrometer that provides global measurements of atmospheric properties and constituents on a daily basis. It is contributing to monitoring air quality and climate, providing critical information to services and decision makers. The instrument uses passive remote sensing techniques by measuring the top of atmosphere solar radiation reflected by and radiated from the earth and its atmosphere. The four spectrometers of TROPOMI cover the ultraviolet (UV), visible (VIS), Near Infra-Red (NIR) and Short Wavelength Infra-Red (SWIR) domains of the electromagnetic spectrum. The operational trace gas products generated at DLR on behave ESA are: Ozone (O3), Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2), Sulfur Dioxide (SO2), Formaldehyde (HCHO), Carbon Monoxide (CO) and Methane (CH4), together with clouds and aerosol properties. This product is created in the scope of the project INPULS. It develops (a) innovative retrieval algorithms and processors for the generation of value-added products from the atmospheric Copernicus missions Sentinel-5 Precursor, Sentinel-4, and Sentinel-5, (b) cloud-based (re)processing systems, (c) improved data discovery and access technologies as well as server-side analytics for the users, and (d) data visualization services.
-

This product displays the Cloud Optical Thickness (COT) around the globe. Clouds play a crucial role in the Earth's climate system and have significant effects on trace gas retrievals. The cloud optical thickness is retrieved from the O2-A band using the ROCINN algorithm. The TROPOMI instrument aboard the SENTINEL-5P space craft is a nadir-viewing, imaging spectrometer covering wavelength bands between the ultraviolet and the shortwave infra-red. TROPOMI's purpose is to measure atmospheric properties and constituents. It is contributing to monitoring air quality and providing critical information to services and decision makers. The instrument uses passive remote sensing techniques by measuring the Top Of Atmosphere (TOA) solar radiation reflected by and radiated from the earth and its atmosphere. The four spectrometers of TROPOMI cover the ultraviolet (UV), visible (VIS), Near Infra-Red (NIR) and Short Wavelength Infra-Red (SWIR) domains of the electromagnetic spectrum, allowing operational retrieval of the following trace gas constituents: Ozone (O3), Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2), Sulfur Dioxide (SO2), Formaldehyde (HCHO), Carbon Monoxide (CO) and Methane (CH4). Within the INPULS project, innovative algorithms and processors for the generation of Level 3 and Level 4 products, improved data discovery and access technologies as well as server-side analytics for the users are developed.
 www.geodatenkatalog.de (S1L)
www.geodatenkatalog.de (S1L)