Contact for the resource
Bundesanstalt für Geowissenschaften und Rohstoffe (BGR)
1033 record(s)
Provided by
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Update frequencies
Service types
-
Storage of CO2 in deep geological formations is one possibility of reducing CO2 emissions from industry that are difficult to avoid. High-quality geological models and capacity estimates are crucial for the successful planning and implementation of safe storage projects. This study analyses the storage potential of the Middle Buntssandstein (Lower Triassic) and Lower to Middle Jurassic within the Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) of the German North Sea. Link https://geostor.cdrmare.de/
-

Compilation of the European Quaternary marine geology (section of Germany). The original map consists of data at highest available spatial resolution, map scale („multi-resolution“-concept) and data completeness vary depending on the project partner (as of 2019 April). Project partners are the national geological services of the participating countries. According to the Data Specification on Geology (D2.8.II.4_v3.0) the geological map (section of Germany) provides INSPIRE-compliant data. The WMS EMODnet-DE Quaternary (INSPIRE) contains layers of the geologic units (GE.GeologicUnit) displayed correspondingly to the INSPIRE portrayal rules. The geologic units are represented graphically by stratigraphy (GE.GeologicUnit.AgeOfRocks) and lithology (GE.GeologicUnit.Lithology). The portrayal of the lithology is defined by the first named rock. Via the getFeatureInfo request the user obtains detailed information on the lithology, stratigraphy (age) and genesis (event environment and event process).
-
.png)
The WMS D-AERO (INSPIRE) comprises airborne geophysical surveys for mapping the shallow subsurface in Germany. Since the eighties BGR carries out helicopter borne measurements in Germany as well as in neighbouring and distant countries. In particular a series of continuous areas on the German North Sea coast are flown during the last years within the context of the D-AERO project. The helicopter of type Sikorsky S-76B is operated for the airborne geophysical survey of the earth's subsurface. Usually airborne electromagnetic, magnetic and radiometric measurements are carried out. According to the Data Specification on Geology (D2.8.II.4_v3.0, sub-theme Geophysics) the information with respect to the airborne geophysical surveys is INSPIRE-compliant. The WMS D-AERO (INSPIRE) contains for each airborne geophysical survey one layer, e.g. GE.flightLine.G081Cuxhaven. The flightlines are displayed correspondingly to the INSPIRE portrayal rules. Via the getFeatureInfo request, the user obtains the content of the INSPIRE attributes platformType und profileType. Additionally, the WMS contains a campaign layer (GE.airborneGeophysicalSurvey) with the INSPIRE attributes campaignType and surveyType.
-
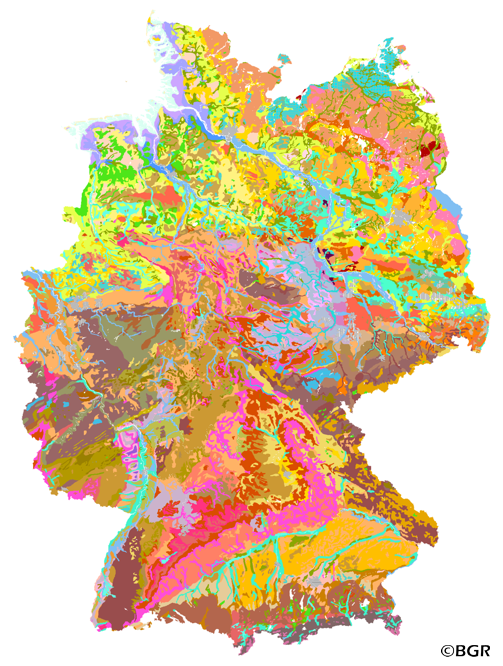
Web Map Service (WMS) of the BUEK1000. The first country wide soil map at a scale of 1:1,000,000 (BUEK1000) has been compiled on the basis of published soil maps of the former German Democratic Republic and the pre 1990 federal states of Germany. To do this, it was necessary to match the soil systems used in East and West Germany and to develop standardized descriptions of soil units. A relatively homogeneous map has resulted, which permits uniform assessment of the soils throughout Germany. The map shows 71 soil mapping units, described in the legend on the basis of the German and FAO soil systems. Each soil unit has been assigned a characteristic soil profile (Leitprofil) as an aid to map interpretation. For the first time the subdivision of the country into 12 soil regions has been represented on the map. This subdivision was coordinated with the state Geological Surveys. These soil regions will represent the highest hierarchic level of nation wide soil maps in future. The colours of soil units correspond to the standards of the 'Bodenkundliche Kartieranleitung' (KA 3; Guidelines for Soil Mapping). The various hues characterize differences in relief or soil humidity. The BUEK1000 was produced digitally. It is an important part of the spatial database integrated in the Soil Information System currently being established at the Federal Institute for Geosciences and Natural Resources (FISBo BGR). It can be used together with the characteristic soil profiles to derive thematic maps related to nation wide soil protection. The scale of the BUEK1000 makes it especially suitable for small scale evaluations at federal or EU level.
-
The WMS SuK-Nord (INSPIRE) shows the geological distribution of aggregates (sand and gravel) in Northern Germany, especially north of the southernmost maximum of the Scandinavian inland ice sheet (Saalian and Elsterian glaciation). According to the Data Specification on Mineral Resources (D2.8.III.21) and Geology (D2.8.II.4_v3.0) the map provides INSPIRE-compliant data. The WMS GK2000 Lagerstätten (INSPIRE) contains the following layers: MR.MineralOccurence.Commodity represents the distribution of sand and gravel. GE.GeomorphologicFeature shows the southernmost maximum of the Scandinavian inland ice sheet (Saalian and Elsterian glaciation).
-
The General Geological Map of the Federal Republic of Germany 1:200,000 (GÜK200) provides detailed information on the stratigraphy, petrography and genesis of the geological units shown. In this revised GÜK200-DN, the onshore surface geology is shown in up to two overlays. The thin overlying soil is not shown. In the marine environment, only the petrography of the recent seabed is shown, which comprises the uppermost 20 cm of the seabed. In accordance with the original GÜK200 map sheets, the seabed is referred to stratigraphically as the recent seabed. According to the Data Specification on Geology (D2.8.II.4_v3.0) the geological map provides INSPIRE-compliant data. A base layer and two overlay layers are displayed correspondingly to the INSPIRE portrayal rules. The geologic units are represented graphically by stratigraphy (GE.GeologicUnit.BaseLayer.AgeOfRocks, GE.GeologicUnit.OverlayLayer1.AgeOfRocks, and GE.GeologicUnit.OverlayLayer2.AgeOfRocks) and lithology (GE.GeologicUnit.BaseLayer.Lithology, GE.GeologicUnit.OverlayLayer1.Lithology, and GE.GeologicUnit.OverlayLayer2.Lithology). The user obtains detailed information via the getFeatureInfo request on the lithology, stratigraphy (age) and genesis (event environment and event process).
-
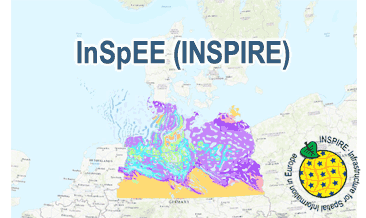
The WMS InSpEE (INSPIRE) provides information about the areal distribution of salt structures (salt domes and salt pillows) in Northern Germany. Contours of the salt structures can be displayed at horizontal cross-sections at four different depths up to a maximum depth of 2000 m below NN. The geodata have resulted from a BMWi-funded research project “InSpEE” running from the year 2012 to 2015. The acronym stands for "Information system salt structures: planning basis, selection criteria and estimation of the potential for the construction of salt caverns for the storage of renewable energies (hydrogen and compressed air)”. Taking into account the fact that this work was undertaken at a scale for providing an overview and not for investigation of single structures, the scale of display is limited to a minimum of 1:300.000. Additionally four horizontal cross-section maps display the stratigraphical situation at a given depth. In concurrence of maps at different depths areal bedding conditions can be determined, e.g. to generally assess and interpret the spread of different stratigraphic units. Clearly visible are extent and shape of the salt structures within their regional context at the different depths, with extent and boundary of the salt structures having been the main focus of the project. Four horizontal cross-section maps covering the whole onshore area of Northern Germany have been developed at a scale of 1:500.000. The maps cover the depths of -500, -1000, -1500, -2000 m below NN. The four depths are based on typical depth requirements of existing salt caverns in Northern Germany, mainly related to hydrocarbon storage. The shapes of the structures show rudimentary information of their geometry and their change with depths. In addition they form the starting point for rock mechanical calculations necessary for the planning and construction of salt caverns for storage as well as for assessing storage potentials. The maps can be used as a pre-selection tool for subsurface uses. It can also be used to assess coverage and extension of salt structures. Offshore areas were not treated within the project. All horizontal cross-section maps were adjusted with the respective state geological survey organisations. According to the Data Specification on Geology (D2.8.II.4_v3.0) the WMS InSpEE (INSPIRE) provides INSPIRE-compliant data. The WMS InSpEE (INSPIRE) contains two group layers: The first group layer “INSPIRE: Salt structures in Northern Germany“ comprises the layers GE.Geologic.Unit.Salt structure types, GE.GeologicUnit.Salt pillow remnants, GE.GeologicUnit.Structure-building salinar and GE.GeologicUnit.Structural outlines. The layer GE.GeologicUnit.Structural outlines contains according to the four depths four sublayers, e.g. GE.GeologiUnit.Structural outlines 500 m below NN. The second group layer „INSPIRE: Horizontal cross-section maps of Northern Germany“ comprises according to the four depths four layers, e.g. Horizontal cross-section map – 500 m below NN. This layer, in turns, contains two sublayers: GE.GeologicFault.Relevant fault traces and GE.GeologicUnit.Stratigraphic Units. Via the getFeatureInfo request the user obtains additional information on the different geometries. In case of the GE.Geologic.Unit.Salt structure types the user gets access to a data sheet with additional information and further reading in German for the respective salt structure via the getFeatureInfo request.
-
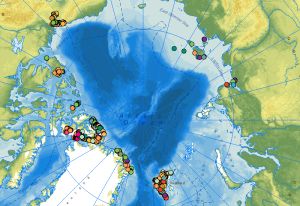
The web service of the dataset comprises the locations of outcrops with respective information on the lithology, stratigraphy, rock age and tectonic data collected during the CASE expeditions. The data attributes include stereographic projections and sketches of tectonic structures derived from the outcrop data. At the end of the 1980s, BGR initiated the research program Circum-Arctic Structural Events (CASE) to reconstruct the plate tectonic processes during the evolution of the Arctic Ocean using terrestrial data from the surrounding continental margins. One of the scientific questions of the CASE programme is as simple as it is complex: How did the Arctic Ocean, this large basin between the Eurasian and North American continental plates, develop? There are still no conclusive answers to this question in terms of plate tectonics. In contrast to the marine expeditions of geophysicists in the Arctic Ocean, geologists on land along the various coastal areas of the Arctic Ocean can directly touch, examine and map rocks, structures, folds and fault zones and determine the respective ages of the movements. This makes it possible to directly compare rock units and deformation zones on different continental plates and thus also to reconstruct when these plates collided, how long they remained next to each other and when and how they separated again. Since the inception of BGR’s Arctic research, the primary focus and research areas have been along the continental margins between Spitsbergen and the Canadian Arctic Archipelago via Greenland, to the Yukon North Slope on the border with Alaska. On the opposite side of the Arctic Ocean, there have been expeditions to Yakutia, the mainland areas near the Laptev Sea, the New Siberian Islands and to the Polar Ural with Russian partners. An important method for the interpretation of the geological evolution of the Arctic is the examination of tectonic structures (faults, folds, cleavage etc.), the determination of the kinematics and the age of the tectonic movements.
-

The IGME5000-EU (INSPIRE) represents the pre-quaternary bedrock geology (onshore and offshore) of the European map on a scale of 1:5,000,000. According to the Data Specification on Geology (D2.8.II.4_v3.0) the geological map provides INSPIRE-compliant data. The WMS IGME5000-EU contains layers of the geologic units (GE.GeologicUnit) and faults (GE.GeologicFault) mostly displayed according to the INSPIRE portrayal rules. The geologic units are represented graphically by stratigraphy (GE.GeologicUnit.AgeOfRocks) and lithology (GE.GeologicUnit.Lithology). For different geochronologic minimum and maximum ages, e.g. Ordovician - Silurian, the portrayal is defined by the color of the geochronologic minimum age (olderNamedAge). The portrayal of the lithology is defined by the first named rock or rock group. In case of the geologic units the user obtains detailed information via the getFeatureInfo request on the lithology and stratigraphy (age).
-

Which salt formations are suitable for storing hydrogen or compressed air? In the InSpEE-DS research project, scientists developed requirements and criteria for the assessment of suitable sites even if their exploration is still at an early stage and there is little knowledge of the salinaries’ structures. Scientists at DEEP.KBB GmbH in Hanover, worked together with their project partners at BGR and the Leibniz University Hanover, Institute for Geotechnics, to develop the planning basis for the site selection and for the construction of storage caverns in flat layered salt and multiple or double saliniferous formations. Such caverns could store renewable energy in the form of hydrogen or compressed air. While the previous project InSpEE was limited to salt formations of great thickness in Northern Germany, salt horizons of different ages have now been examined all over Germany. To estimate the potential, depth contour maps of the top and the base as well as thickness maps of the respective stratigraphic units were developed. Due to the present INSPIRE geological data model, it was necessary, in contrast to the original dataset, to classify the boundary lines of the potential storage areas in the Zechstein base and thickness layers, whereby the classification of these lines was taken from the top Zechstein layer. Consequently, the boundary element Depth criterion 2000 m (Teufe-Kriterium 2000 m) corresponds on each level to the 2000 m depth of Top Zechstein. However, the boundary of national borders and the boundary of the data basis could not be implemented in the data model and are therefore not included in the dataset. Information on compressed air and hydrogen storage potential is given for the identified areas and for the individual federal states. According to the Data Specification on Geology (D2.8.II.4_v3.0) the content of InSpEE-DS (INSPIRE) is stored in 18 INSPIRE-compliant GML files: InSpEE_DS_GeologicUnit_Isopachs_Zechstein.gml contains the Zechstein isopachs. InSpEE_DS_GeologicUnit_Isobaths_Top_Zechstein.gml and InSpEE_DS_GeologicUnit_Isobaths_Basis_Zechstein.gml contain the isobaths of the top and basis of Zechstein. The three files InSpEE_DS_GeologicStructure_ThicknessMap_Zechstein, InSpEE_DS_GeologicStructure_Top_Zechstein and InSpEE_DS_GeologicStructure_Basis_Zechstein represent the faults of the Zechstein body as well as at the top and at the basis of the Zechstein body. InSpEE_DS_GeologicUnit_Boundary_element_Potential_areas_Zechstein.gml contains the boundary elments of the potential areas at the top and the basis of Zechstein as well as of the Zechstein body. The three files InSpEE_DS_GeologicUnit_Uncertainty_areas_ThicknessMap_Zechstein.gml, InSpEE_DS_GeologicUnit_Uncertainty_areas_Top_Zechstein.gml, InSpEE_DS_GeologicUnit_Uncertainty_areas_Basis_Zechstein.gml represent the uncertainty areas of the Zechstein body as well as at the top and at the basis of the Zechstein body. InSpEE_DS_GeologicUnit_Potentially_usable_storage_areas_Storage_potential_in_the_federal_states.gml comprises the areas with storage potential for renewable energy in the form of hydrogen and compressed air. The six files InSpEE_DS_GeologicUnit_Salt_distribution_in_Germany_Malm.gml, InSpEE_DS_GeologicUnit_Salt_distribution_in_Germany_Keuper.gml, InSpEE_DS_GeologicUnit_Salt_distribution_in_Germany_Muschelkalk.gml, InSpEE_DS_GeologicUnit_Salt_distribution_in_Germany_Roet.gml, InSpEE_DS_GeologicUnit_Salt_distribution_in_Germany_Zechstein.gml and InSpEE_DS_GeologicUnit_Salt_distribution_in_Germany_Rotliegend.gml represent the salt distribution of the respective stratigraphic unit. InSpEE_DS_GeologicUnit_General_salt_distribution.gml represents the general salt distribution in Germany. This geographic information is product of a BMWi-funded research project "InSpEE-DS" running from the year 2015 to 2019. The acronym stands for "Information system salt: planning basis, selection criteria and estimation of the potential for the construction of salt caverns for the storage of renewable energies (hydrogen and compressed air) - double saline and flat salt layers".
 www.geodatenkatalog.de (S1L)
www.geodatenkatalog.de (S1L)