Keyword
Geoscientific information
3857 record(s)
Provided by
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Update frequencies
Service types
-
For the individual erosion events, the thicknesses to be eroded were determined from the initial thickness of a sequence. These maps were smoothed again, e.g. in the marginal depressions of the salt diapirs to avoid abrupt thickness transitions. The maps of eroded thicknesses were calculated from the maps of initial thickness of the respective sequence. The initial thickness of a sedimentary layer was determined for the Jurassic and Triassic strata by our own estimates from the missing thicknesses in the area of the salt domes and from calibrated 1D models; for the Carboniferous Stefan and Westfal horizons they were taken from Krull (2005). Initial thickness maps for the Carboniferous sediments were created from the printed maps by scanning, georeferencing, digitizing isolines, and interpolating to a contiguous surface. Maps of eroded thicknesses were then calculated in PetroMod modeling software (Schlumberger, version 2012.2). The amount of erosion is calculated by subtracting the residual thickness (today) from the initial thickness. Since in the hydrocarbon model the salt movement was modeled parallel to the erosion events, it was necessary to correct the calculated erosion amounts or maps finally to avoid horizon overlaps and abrupt cell transitions. For this reason, both sets of maps (initial and eroded thicknesses) are available for download. The maps are available in two different data formats (CPS3 and Zmap). The individual thickness maps have a file size of 8.5 MB each (zip files 0.3 to 1.4 MB).
-
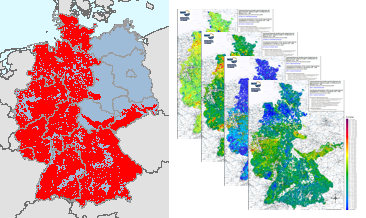
Between 1975 and 1986, geochemical investigations were carried out by the Federal Institute for Geosciences and Natural Resources (BGR) on the territory of the then Federal Republic of Germany and by the Central Geological Institute (ZGI) of the former GDR in the area of the pre-Upper Permian bedrock units in the southern part of the former GDR, which lie on the earth's surface or are slightly covered by the Cenozoic. Approximately 98,000 water and 87,500 stream sediment samples were taken and geochemically analysed. The results of these investigations were published in the "Geochemical Atlas of the Federal Republic of Germany" (Fauth et al., 1985) and in the "Final Report on the Comparative Evaluation of the Raw Material Potential in the Bedrock Units of the GDR" (Röllig et al., 1990; in German). The geochemical data collected as part of these investigations, which cover a large part of the area of today's Federal Republic of Germany, are unique in their high sampling density. All subsequent geochemical investigations were carried out with a much lower sample density. These valuable and irretrievable data have been generally accessible via the BGR geoportal since their digital processing and provision in 2022 (Geochemical Atlas of the Federal Republic of Germany) and 2023 (Geochemical Prospection in the bedrock units in the southern part of the former GDR). However, a direct comparison of the maps produced for the two sub-areas is not possible due to the differences in the analytical methods used in the investigations (investigated element spectrum, analytical quality, determination limits, ...). Nevertheless, for some of the investigated elements and parameters it is possible to summarise the results of these geochemical investigations, which are unique in their high occupancy density, with appropriate adjustments (determination limits, representable content ranges, classification of the map legends, ...). Such summarised representations are now being made available for the first time via the BGR geoportal. The downloads show the distribution of Fluoride contents in stream waters in four different coloured point and colour shaded contour maps.
-
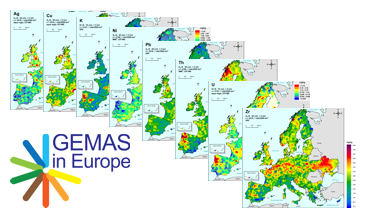
GEMAS (Geochemical Mapping of Agricultural and Grazing Land Soil in Europe) is a cooperative project between the Geochemistry Expert Group of EuroGeoSurveys and Eurometeaux. In total, more than 60 international organisations and institutions worldwide were involved in the implementation of the project. During 2008 and 2009, a total of 2219 samples of agricultural (arable land soils, 0 – 20 cm, Ap samples) and 2127 samples of grazing land (pasture land soils, 0 – 10 cm, Gr samples) soil were collected at a density of 1 site/2 500 km² each from 33 European countries, covering an area of 5,600,000 km². In addition to the chemical element contents, soil properties and soil parameters such as pH, particle size distribution, effective cation exchange capacity (CEC), MIR spectra and magnetic susceptibility were investigated in the samples and some coefficients were calculated. The downloadable files present the areal distribution of the determined RCR (risk characterisation ratio) for Copper (Cu) in the shape of colour shaded contour maps.
-
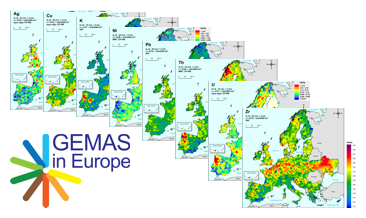
GEMAS (Geochemical Mapping of Agricultural and Grazing Land Soil in Europe) is a cooperative project between the Geochemistry Expert Group of EuroGeoSurveys and Eurometeaux. In total, more than 60 international organisations and institutions worldwide were involved in the implementation of the project. During 2008 and 2009, a total of 2219 samples of agricultural (arable land soils, 0 – 20 cm, Ap samples) and 2127 samples of grazing land (pasture land soils, 0 – 10 cm, Gr samples) soil were collected at a density of 1 site/2 500 km² each from 33 European countries, covering an area of 5,600,000 km². All samples were analysed for 52 chemical elements after an aqua regia extraction, 41 by XRF (total), TC and TOC. In addition, the agricultural soil samples were analysed for 57 elements in a mobile metal ion (MMI®) extraction and Pb isotopes. All analytical results were subject to tight external quality control procedures. The GEMAS project thus provides for the first time fully harmonised data for element concentrations and bioavailability of the elements at the continental (European) scale. The downloadable files present the areal distribution of the element contents determined by different analytical methods in the shape of colour shaded contour maps with a classification in 7 and 72 levels each.
-
The International Geological Map of Europe and the Mediteranean Regions 1 : 1 500 000 ("Carte Géologique Internationale de l'Europe et des Régions Méditerranéennes 1 : 1 500 000") shows the geology of the European continent from the Ural mountains in the east up to Island in the west and the whole mediteranean region in the south. The geology is differenciated in stratigraphy, igneous and metamorphic rocks. In addition there are two legend sheets and a title sheet. The language of the series is French.
-

Between 1975 and 1986, geochemical investigations were carried out by the Federal Institute for Geosciences and Natural Resources (BGR) on the territory of the then Federal Republic of Germany and by the Central Geological Institute (ZGI) of the former GDR in the area of the pre-Upper Permian bedrock units in the southern part of the former GDR, which lie on the earth's surface or are slightly covered by the Cenozoic. Approximately 98,000 water and 87,500 stream sediment samples were taken and geochemically analysed. The results of these investigations were published in the "Geochemical Atlas of the Federal Republic of Germany" (Fauth et al., 1985) and in the "Final Report on the Comparative Evaluation of the Raw Material Potential in the Bedrock Units of the GDR" (Röllig et al., 1990; in German). The geochemical data collected as part of these investigations, which cover a large part of the area of today's Federal Republic of Germany, are unique in their high sampling density. All subsequent geochemical investigations were carried out with a much lower sample density. These valuable and irretrievable data have been generally accessible via the BGR geoportal since their digital processing and provision in 2022 (Geochemical Atlas of the Federal Republic of Germany) and 2023 (Geochemical Prospection in the bedrock units in the southern part of the former GDR). However, a direct comparison of the maps produced for the two sub-areas is not possible due to the differences in the analytical methods used in the investigations (investigated element spectrum, analytical quality, determination limits, ...). Nevertheless, for some of the investigated elements and parameters it is possible to summarise the results of these geochemical investigations, which are unique in their high occupancy density, with appropriate adjustments (determination limits, representable content ranges, classification of the map legends, ...). Such summarised representations are now being made available for the first time via the BGR geoportal. The downloads show the distribution of the sample points and the sampled area in the form of a (smoothed) buffer around the sample points.
-
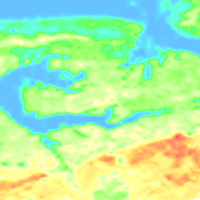
BGR conducted an airborne survey in the region of the Ahlenmoor (Lower Saxony) as part of the BGR project D-AERO-Moore. Cunducting tests of their airborne system, the BGR surveys a portion of the Ahlenmoor with the BGR airborne geophysical standard measuring system. The peatland is located about 15 km northeast of the city of Bremerhaven close to Ahlen-Falkenberg. The size of the area is about 15 km². The area was surveyed with 2 flights totalling to 105 line-km (2,899 survey points). The nominal separation of the 16 WNW-ESE lines and 2 NNE-SSW tie lines was 125 m and 2000 m, respectively. The maps display the total count, the (equivalent) content of potassium, uranium and thorium as well as the exposure rate at ground.
-

Between 1975 and 1986, geochemical investigations were carried out by the Federal Institute for Geosciences and Natural Resources (BGR) on the territory of the then Federal Republic of Germany and by the Central Geological Institute (ZGI) of the former GDR in the area of the pre-Upper Permian bedrock units in the southern part of the former GDR, which lie on the earth's surface or are slightly covered by the Cenozoic. Approximately 98,000 water and 87,500 stream sediment samples were taken and geochemically analysed. The results of these investigations were published in the "Geochemical Atlas of the Federal Republic of Germany" (Fauth et al., 1985) and in the "Final Report on the Comparative Evaluation of the Raw Material Potential in the Bedrock Units of the GDR" (Röllig et al., 1990; in German). The geochemical data collected as part of these investigations, which cover a large part of the area of today's Federal Republic of Germany, are unique in their high sampling density. All subsequent geochemical investigations were carried out with a much lower sample density. These valuable and irretrievable data have been generally accessible via the BGR geoportal since their digital processing and provision in 2022 (Geochemical Atlas of the Federal Republic of Germany) and 2023 (Geochemical Prospection in the bedrock units in the southern part of the former GDR). However, a direct comparison of the maps produced for the two sub-areas is not possible due to the differences in the analytical methods used in the investigations (investigated element spectrum, analytical quality, determination limits, ...). Nevertheless, for some of the investigated elements and parameters it is possible to summarise the results of these geochemical investigations, which are unique in their high occupancy density, with appropriate adjustments (determination limits, representable content ranges, classification of the map legends, ...). Such summarised representations are now being made available for the first time via the BGR geoportal. The downloads show the distribution of Lithium contents in stream sediments in four different coloured point and colour shaded contour maps.
-
Between 1977 and 1983, the Federal Institute for Geosciences and Natural Resources (BGR) took approx. 80,000 water samples and 70,000 sediment samples from streams and rivers in several sampling campaigns on the territory of the Federal Republic of Germany at that time and examined them geochemically. In addition to the geochemical prospection of areas with potentially deposits, the aim of the investigations was also to record indications of anthropogenic environmental pollution. The results of these investigations were published in the Geochemical Atlas of the Federal Republic of Germany (Fauth et al., 1985). The data collected within the framework of the Geochemical Atlas of the Federal Republic of Germany in 1985 is a geochemical survey of the former territory of the Federal Republic of Germany which is unique in its high sampling density. All later geochemical investigations were carried out with a much lower sampling density. This valuable and irretrievable data is now being made generally available via the BGR geoportals. In addition to the digital provision of the original data material, the texts from Fauth et al. (1985) and distribution maps produced according to the method used in 1985, the data were reprocessed using modern methods. The downloads show the distribution of Cobalt concentrations in stream waters in five different coloured point and colour shaded contour maps. In addition, the brief explanations on the element Cobalt from Fauth et al. (1985) are included.
-
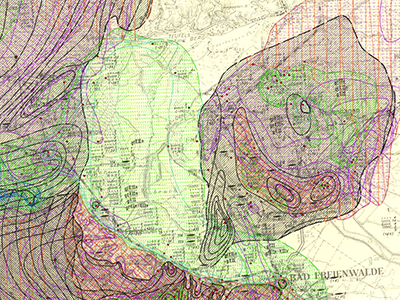
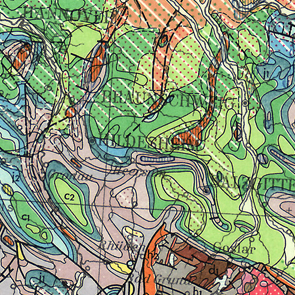
The Lithofacial Map of the Quaternary 1 : 50,000 (LKQ 50) is a map series of the GDR covering nearly the whole former state territory besides the South of Saxony and Thuringia. The series consists of 123 map sheets, each of which encompassing several horizon maps mostly complemented by about five cross sections. Specifications concerning map content and structure provides Cepek (1999). The data of the LKQ 50 map sheet 1869 Bad Freienwalde provided here were digitised in frame of the Geo3D-Oder project of the German Federal Institute for Geosciences and Natural Resources (BGR). The data include elements of the five horizon maps 1869-2, 1869-3, 1869-4, 1869-5 and 1869-6 and of the five cross sections Schnitt 1 to Schnitt. The topics of these maps and cross sections are defined in a general legend (version 3). Furthermore, the legends of the single horizon maps provide a stratigraphic and genetic classification of the depicted strata. For each horizon map the digitised elements comprise several polygon shapefiles of the single layers, a polyline shapefile of isohypses related to layer bases, a point shapefile of lithological profiles and a polygon shapefile of additional information concerning areas of heavy strata deformation and insufficient investigation. The data of each cross section includes a polygon shapefile of the horizon section areas, a polygon shapefile of the section areas concerning regions with heavy layer deformation or insufficient investigation and a shapefile showing the transect line to locate the cross section. Non-numeric contents of the attribute tables are encoded by numbers and are translated in full text by means of key tables. The key table Normalprofil allows the stratigraphic and genetic classification of horizons displayed in horizon maps by code numbers of the column N_ID. Detailed descriptions concerning the data structure are provided in the attachments. Reference: Cepek, A. G. (1999): Die Lithofazieskarte Quartär 1 : 50.000 (LKQ 50) – Eine Erläuterung des Kartenkonzepts mit Hinweisen zum Gebrauch. - Brandenburgisch. Geowiss. Beitr. 6, 2: 3-38, 3 Abb., 2 Tab.; Kleinmachnow
 www.geodatenkatalog.de (S1L)
www.geodatenkatalog.de (S1L)